자료구조, Linked List 1편, Singly Linked List
Singly Linked List
링크드 리스트(Linked List)
- Sorted List에서 삽입, 삭제 연산을 빠르게 하기 위함
- Sorted List이어도 삽입, 삭제 연산보다 탐색 연산이 빈번하면 Array가 더 유리한 경우가 많음
- array는 연속적인 메모리 주소 마다 item을 저장하는 한편, linked list는 노드 당 1개의 item을 저장하고 각 노드는 다음 노드로 갈 수 있는 포인터를 가지고 있음
- 이때, n번재 item을 탐색하기 위해서는 1번째 포인터, 2번째 포인터, n-1번째 포인터를 모두 거쳐야 하므로 탐색에서는 불리
- iterator 혹은 pointer를 통한 삽입, 삭제 연산에서는 유리
- item 값을 통한 탐색 후 삽입, 삭제가 발생하는 경우 시간복잡도 증가
링크드 리스트(Linked List)에 필요한 Operator
- Constructor
- Linked List 객체 생성을 위한 생성자
- Destructor
- Linked List 객체 삭제를 위한 소멸자
- Transformer
- Linked List의 상태를 변환하는 변환자
- Observer
- Linked List의 아이템이나 길이 등의 정보에 접근하기 위한 관측자
Singly Linked List(SLL)
- Doubly Linked List에 앞서 특수한 상황을 위한 Linked List
- Doubly Linked List는 현재 노드의 전, 후 모두 이동 가능하나, Sigly Linked List는 현재 노드의 후로만 이동 가능
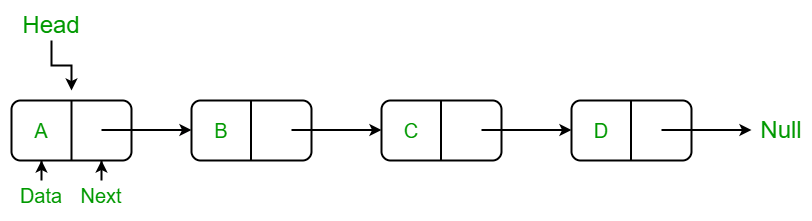
Singly Linked List Search Algorithm
-
위 그림에서 Head를 현재 노드의 Next 포인터를 따라 한 칸씩 이동시키며 탐색
-
3번 째 item을 찾고자 한다면 아래와 같이 코드를 작성할 수 있을 것
- Node라는 별도의 구조체와 SLL이라는 클래스는 이미 있다고 가정하자
Node* cur_node = SLL.get_root(); // cur_node->item == 'A'
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
cur_node = cur_node->next;
}
// 0번째 iteration 종료 시, cur_node->item == 'B'
// 1번째 iteration 종료 시, cur_node->item == 'C'
cout << cur_node->item;
Singly Linked List Insertion Algorithm
Naive Idea
- naive하게 접근해보자
그냥 날로 접근해보자
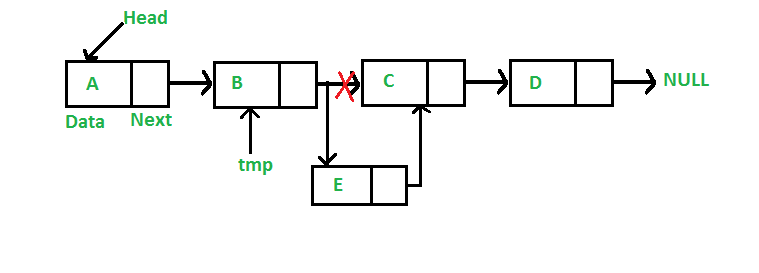
- 새로운 노드를 ‘B’와 ‘C’ 사이에 넣을려고 한다
- 우선 새로운 객체를 생성해야겠지?
- ‘B’노드의 next 포인터는 새로운 객체를 가르켜야 하고
- 새로운 객체의 next 포인터는 ‘C’노드를 가르켜야 한다
- 근데 ‘B’노드의 next 포인터를 먼저 새로운 객체를 가르키고 나니 ‘C’ 노드의 행방이 묘연해졌다.
- 이에 대한 2가지 솔루션이 있다
- Solution 1.
- 무지성으로 접근하면 temp_ptr을 생성해서 ‘C’ 노드로의 포인터를 저장
- Solution 2.
- 반대로 새로운 객체의 next 포인터가 ‘C’를 먼저 가르키게 한 뒤 ‘B’ 노드의 next포인터가 새로운 객체를 가르키게 한다
- 당연히 ‘Solution 2’가 교과서적인 접근이다.
- Solution 1.
- ‘너무 쉽고도 당연한 solution 아닌가?’ 라고 생각될 수 있으나, Doubly Linked List의 Insertion 알고리즘에도 동일하게 적용되는 아이디어이다. 막상 Doubly Linked List를 보면 Insertion의 순서가 마냥 쉽게 떠올르진 않을 것이다. (적어도 나는 그랬다)
Singly Linked List(SLL)에 필요한 Operators
- Constructor
- Destructor
- Transformers
- insert
- erase
- Observers
- Iterator
- operator*
- operator++
- operator==
- operator!=
- GetCurrent
- IsEmpty
- IsFull
- SizeIs
- Iterator
Source Code
Preprocessing
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ItemType;
struct Node;
class SLL;
Node Struct
struct Node {
ItemType item = 0;
Node* next = nullptr;
};
Class Definition
class SLL {
private:
Node* root = nullptr;
size_t size = 0;
public:
class Iterator { //SLL 객체의 아이템 접근을 위한 iterator
private:
Node* current;
Node* previous;
public:
explicit Iterator(Node* node); //iterator 객체 생성자
ItemType& operator*() const; //SLL Node의 item 접근을 위한 연산자 오버로딩
Iterator& operator++(); //SLL iterator가 다음 노드를 지시하도록 하기 위한 연산자 오버로딩
bool operator==(const Iterator& other) const; //SLL iterator가 지시하는 노드가 서로 동일한지 확인하는 연산자
bool operator!=(const Iterator& other) const; //SLL iterator가 지시하는 노드가 서로 다른지 확인하는 연산자
Node* GetCurrent() const; //SLL iterator가 현재 지시하고 있는 노드의 포인터를 반환
Node* GetPrevious() const; //현재 지시하고 있는 노드의 이전 노드의 포인터를 반환
};
explicit SLL(ItemType root_item);
~SLL();
[[nodiscard]] bool IsFull() const; //SLL이 가득 차 있는지 확인
[[nodiscard]] bool IsEmpty() const; //SLL이 비어있는지 확인
[[nodiscard]] int SizeIs() const; //SLL의 크기 반환
void Insert(Iterator pos, ItemType new_item); //SLL에 아이템 삽입
void Erase(Iterator pos); //SLL의 아이템 삭제
[[nodiscard]] Iterator Begin() const { return Iterator(root); } //SLL의 처음 시작위치 반환
[[nodiscard]] Iterator End() const { return Iterator(nullptr); } //SLL의 마지막 위치 반환(nullptr)
};
Iterator Implementation
SLL::Iterator::Iterator(Node* node) : current(node) {}
ItemType& SLL::Iterator::operator*() const {
return current->item;
}
SLL::Iterator& SLL::Iterator::operator++() {
if (current != nullptr) {
previous = current;
current = current->next;
}
return *this;
}
bool SLL::Iterator::operator==(const Iterator &other) const {
return current == other.current;
}
bool SLL::Iterator::operator!=(const Iterator& other) const {
return current != other.current;
}
Node* SLL::Iterator::GetCurrent() const {
return current;
}
Node* SLL::Iterator::GetPrevious() const {
return previous;
}
Constructor
SLL::SLL(const ItemType root_item) {
root = new Node();
root->item = root_item;
root->next = nullptr;
size++;
}
Destructor
SLL::~SLL() {
Node* cur_node = root;
while(cur_node != nullptr) {
Node* temp_ptr = cur_node->next;
delete cur_node;
cur_node = temp_ptr;
}
}
Observer
bool SLL::IsFull() const {
try {
const Node* dummy_node = new Node(); //dummy_node가 생성 가능하면 false 반환
delete dummy_node;
return false;
}
catch(const bad_alloc& e) { //dummy_node가 생성되지 않고 bad_alloc exception 발생
return true; //true 반환
}
}
bool SLL::IsEmpty() const {
return root == nullptr;
}
size_t SLL::SizeIs() const {
return size;
}
Transformer
void SLL::Insert(Iterator pos, ItemType new_item) {
if (IsFull()) {
cerr << "List is Full, bad_alloc exception" << endl;
return;
}
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->item = new_item;
if (pos.GetCurrent() == root) {
new_node->next = root;
root = new_node;
}
else {
Node* prev_node = pos.GetPrevious();
new_node->next = pos.GetCurrent();
if (prev_node != nullptr) {
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
}
size++;
}
void SLL::Erase(Iterator pos) {
if (IsEmpty() || pos.GetCurrent() == nullptr) {
cerr << "List is empty or invalid iterator, nothing to erase." << endl;
return;
}
if (pos.GetCurrent() == root) {
Node* temp_ptr = root;
root = root->next;
delete temp_ptr;
}
else {
Node* prev_node = pos.GetPrevious();
if (prev_node != nullptr) {
prev_node->next = pos.GetCurrent()->next;
delete pos.GetCurrent();
}
}
size--;
}
Main Function
int main() {
SLL list(5);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 10);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 15);
list.Insert(list.Begin(), 20);
cout << "List Size: " << list.SizeIs() << endl;
for (SLL::Iterator it = list.Begin(); it != list.End(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
SLL::Iterator erase_it = list.Begin();
++erase_it;
list.Erase(erase_it);
cout << "List Size after erasing 10: " << list.SizeIs() << endl;
for (SLL::Iterator it = list.Begin(); it != list.End(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
참고문헌
- Nell Dale. (2016). “C++ Plus Data Structues Sixth Edition”. Jones&Bartlett Learning.
- GeeksforGeeks. (2024). “Singly Linked List Data Structure”. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/applications-of-linked-list-data-structure/.
- GeeksforGeeks. (2024). “What are real life exaples of double linked list”. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/what-are-real-life-examples-of-double-linked-list/.
- OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT(Aug 8, 2024). GPT-4o. https://chat.openai.com.
- meongju0o0. (2024). “singly_linked_list.cpp”. https://github.com/meongju0o0/meongju0o0-data-structure.


댓글남기기