[자료구조] 큐(Queue)
큐(Queue)
큐(Queue)
- 데이터들을 줄세운다고 생각하자
- 먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 구조
- 마찬가지로 나중에 들어온 데이터는 나중에 나가는 구조
- FIFO(First In First Out)형태의 자료구조
- 직전에 들어온 데이터는 rear라는 포인터가 지칭
- 큐에서 나가기 직전의 데이터는 front라는 포인터가 지칭
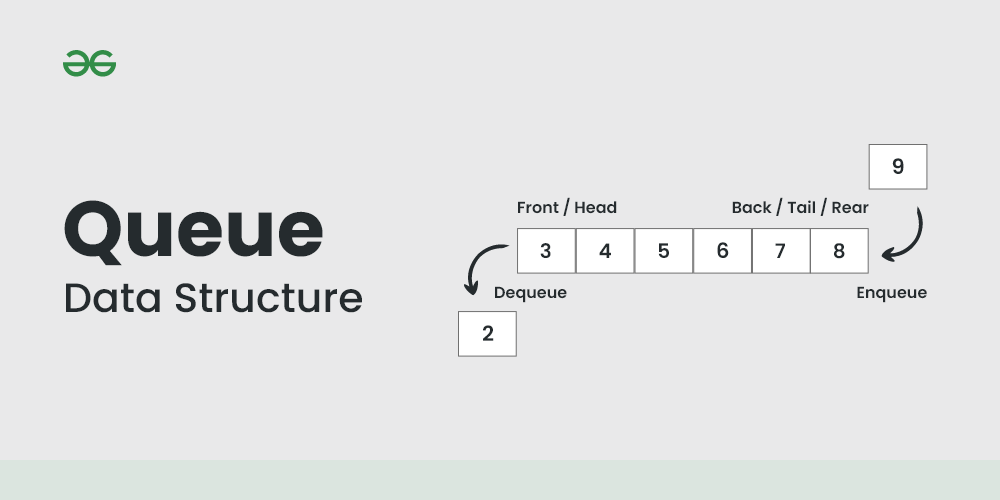
- Enqueue
- rear에서 이루어지는 삽입 연산
- Dequeue
- front에서 이루어지는 삭제 연산
큐(Queue)에 필요한 Operators
- Constructor
- 큐 객체를 생성하는데 필요한 생성자
- Destructor
- 큐 객체를 삭제하는데 필요한 소멸자
- Transformer
- 큐의 상태 (들어있느 아이템의 값 등)을 변환하는 변환자
- Observer
- 큐의 아이템이나 길이 등의 정보에 접근하는 관측자
Problem. Simple Array Based Queue
- 단순히 배열에 큐를 생성하고 rear와 front를 지정하면 문제점 존재
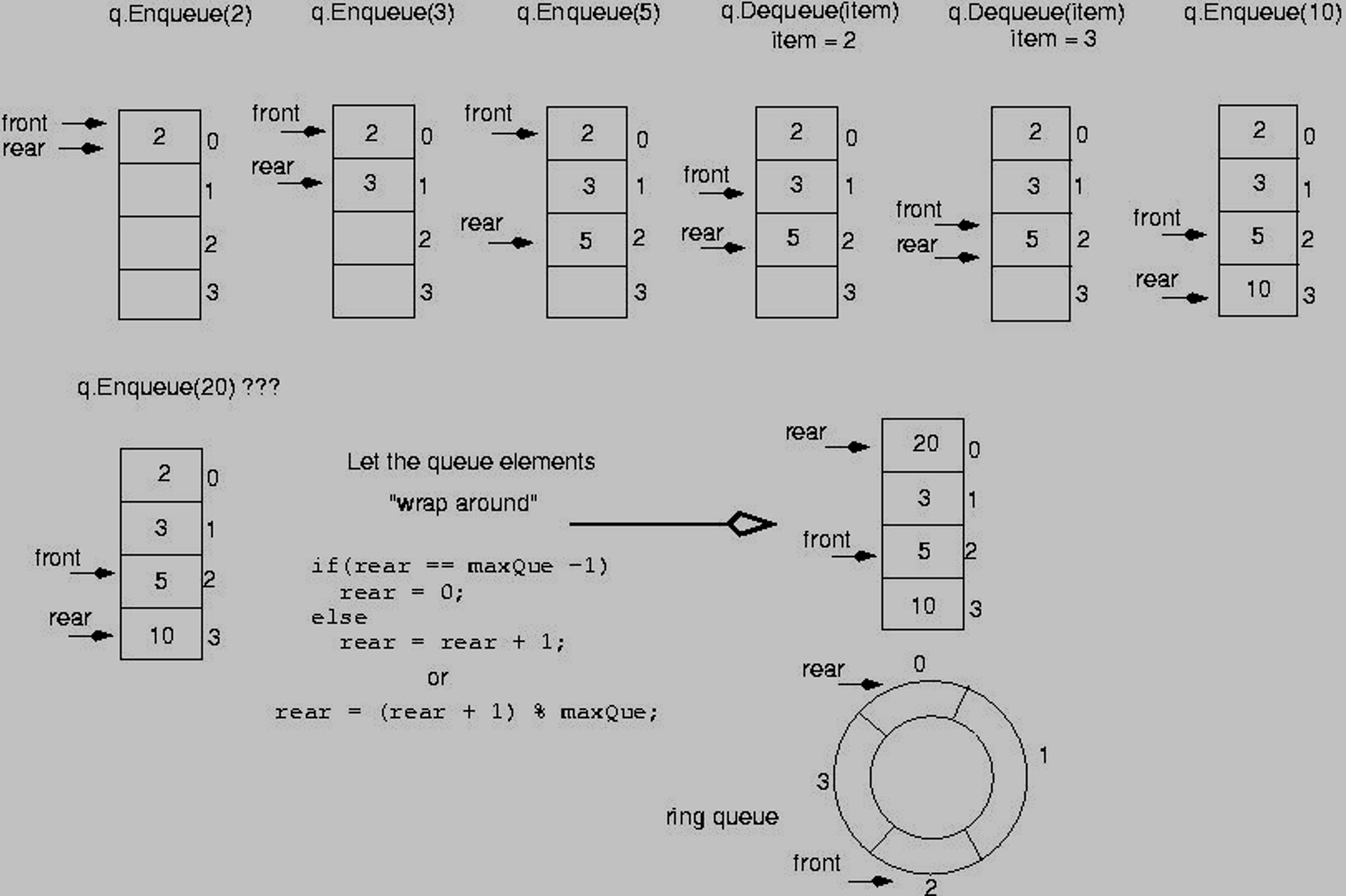
- 위 그림과 같이 실제 할당된 배열의 전체 크기를 활용하지 못한다는 문제점 존재
- 극단적으로, 크기가 4인 배열에서 Enqueue를 4번 수행하고 Dequeue도 4번 수행하면 메모리는 할당 받았지만, 이용할 수 있는 공간이 없음
Solution 1. Circular Queue
- 위 그림에서 3번 주소까지 사용 가능한 모든 공간을 사용한 경우, 다시 0번으로 rear를 설정
- 이를 형상화하면 원형의 모양이 되어서 Circular Queue라 지칭
- 그러나, 해당 기능만 적용 시 다른 문제점 존재
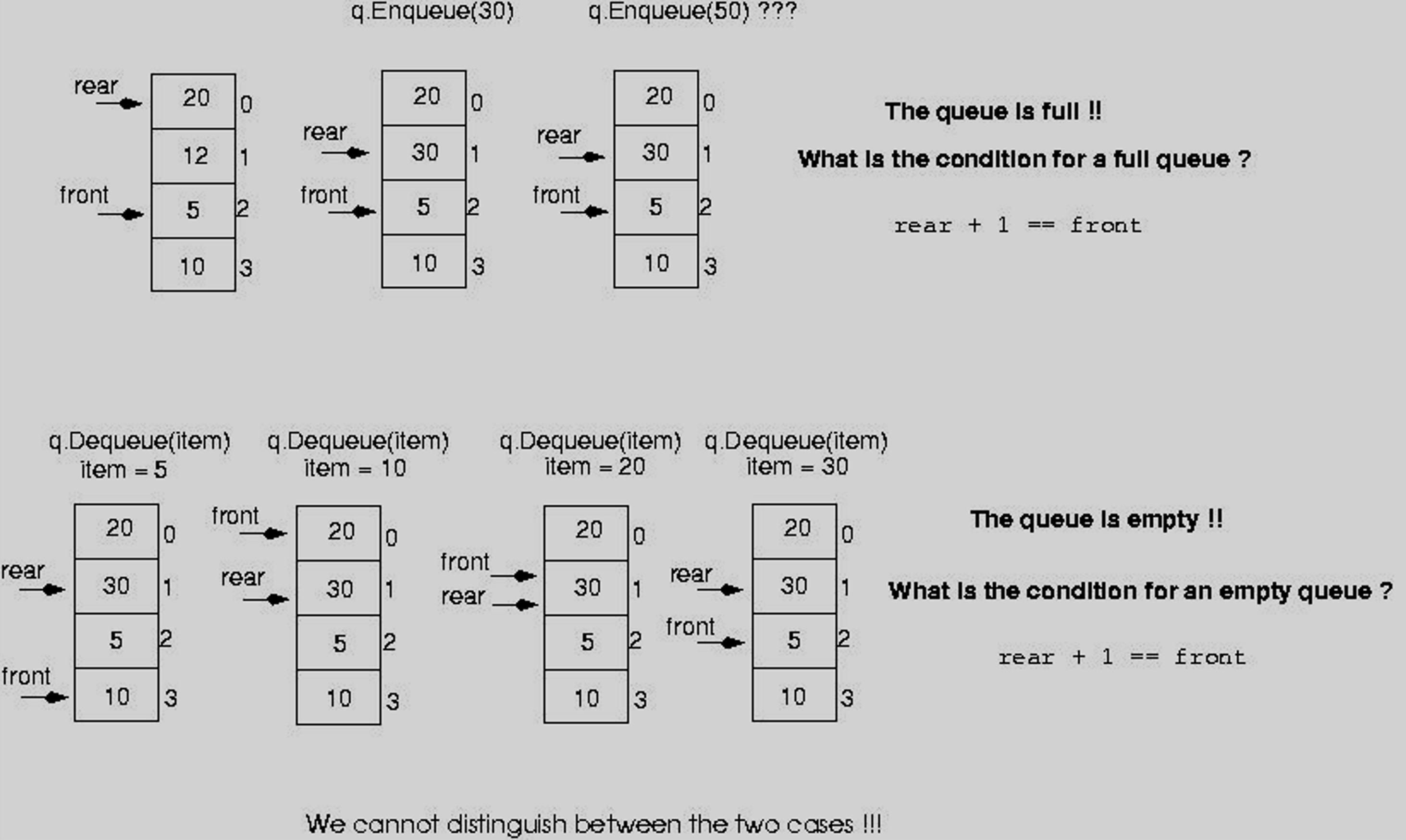
- 기본적으로 rear + 1 == front이면 queue는 가득 찬 상태
- rear는 방금 들어온 아이템
- front는 나가기 직전 (아직은 안 나간 상태)
- 한편, Dequeue를 지속적으로 수행하여 rear의 아이템까지 뱉어낸다고 하자
- Queue의 아이템이 모두 빌때가지 수행하면 마지막 Dequeue 수행시, front++ 연산 수행도 같이 수행
- 두, 세번째 연산으로 인해 queue가 빈 상태 또한 rear + 1 == front
- 기본적으로 rear + 1 == front이면 queue는 가득 찬 상태
- 큐가 가득 찬 상태와 비어있는 상태를 구분할 수 없음
Solution 2. Circular Queue (Final)
- rear까지 Dequeue가 가능하게 만들지 말자!
-
동시에, reserved 공간을 생성하여 front 연산 수행 시 front의 칸을 한칸 뒤로 옮김과 동시에 Dequeue될 값을 reserved로 설정
- 위와 같이 구성하였을 때
- 큐가 가득 차있으면
- rear + 1 = front
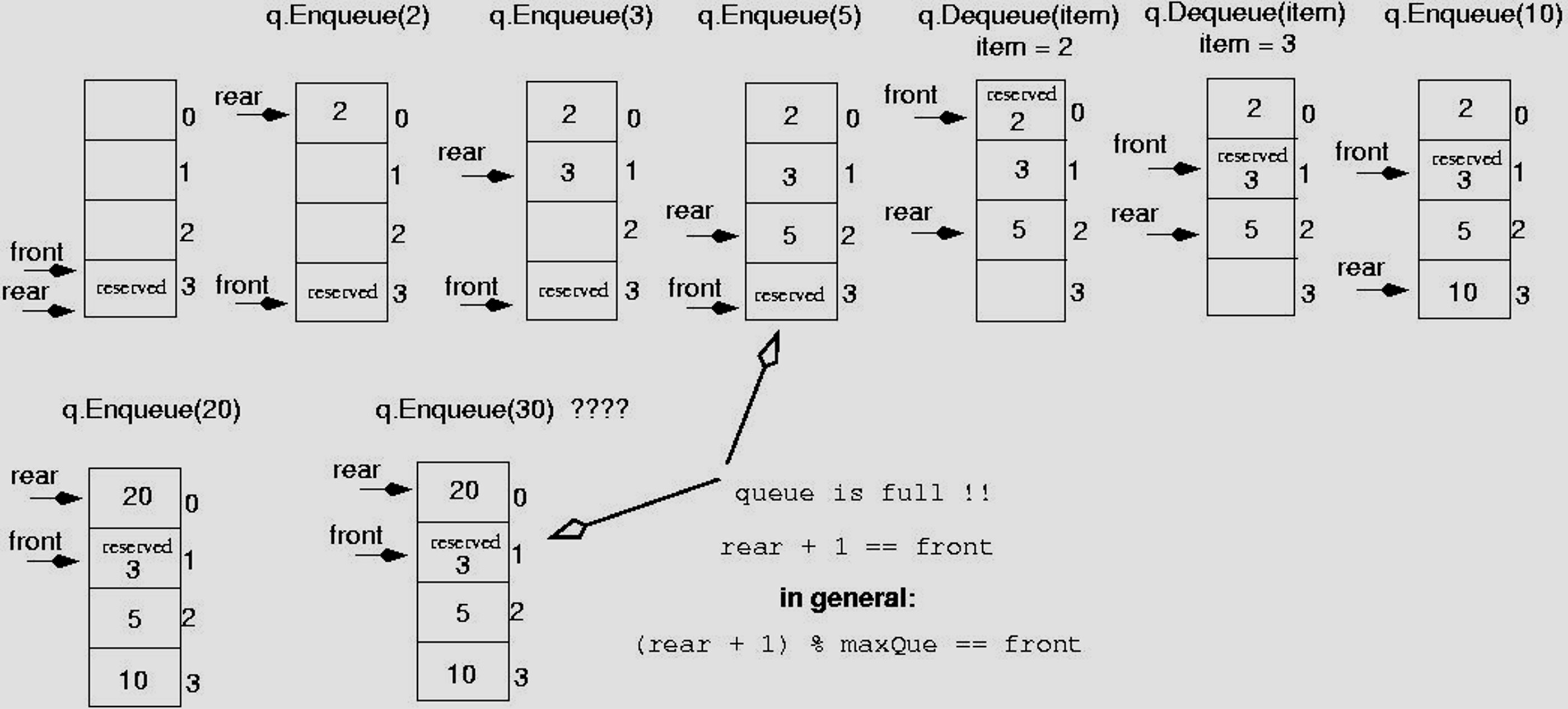
- rear + 1 = front
- 큐가 비어있으면
- (rear + 1) % maxQue == front
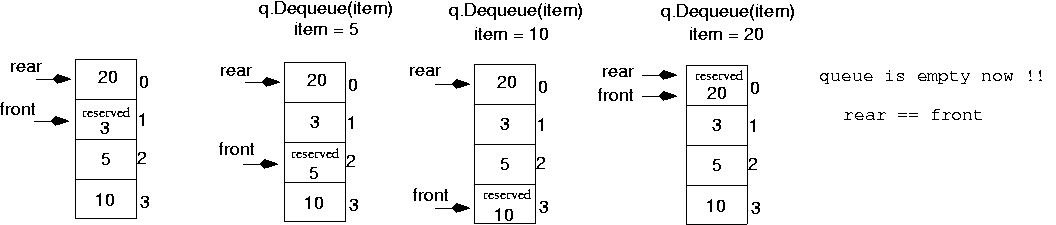
- (rear + 1) % maxQue == front
Queue Operators(Array Based)
- Transformers
- Push
- Pop
- Observers
- IsEmpty
- IsFull
- Top
Source Code
Preprocessing
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#define FULL_QUEUE "queue is full"
#define EMPTY_QUEUE "queue is empty"
using namespace std;
typedef int ItemType;
class QueueType;
Class Definition
class QueueType {
public:
QueueType(int max);
~QueueType();
[[nodiscard]] bool IsFull() const; //큐가 가득 차있는지 확인
[[nodiscard]] bool IsEmpty() const; //큐가 비어있는지 확인
void Enqueue(ItemType newItem); //큐 rear에 아이템 삽입
ItemType Dequeue(); //큐 front의 아이템 삭제 및 반환
private:
int front;
int rear;
int maxQue;
ItemType* items;
};
Constructor
QueueType::QueueType(int max) {
maxQue = max + 1;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}
Destructor
QueueType::~QueueType() {
delete [] items;
}
Observer
bool QueueType::IsEmpty() const {
return rear == front;
}
bool QueueType::IsFull() const {
return (rear + 1) % maxQue == front;
}
Transformer
void QueueType::Enqueue(ItemType newItem) {
if (IsFull()) {
throw runtime_error(FULL_QUEUE);
}
rear = (rear + 1) % maxQue;
items[rear] = newItem;
}
ItemType QueueType::Dequeue() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw runtime_error(EMPTY_QUEUE);
}
front = (front + 1) % maxQue;
return items[front];
}
Main Function
int main() {
QueueType myQueue(5);
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
cout << "Enqueuing " << i << " onto the queue." << endl;
myQueue.Enqueue(i);
}
} catch (const runtime_error& e) {
cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << endl;
}
cout << "Is the queue full? " << (myQueue.IsFull() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
cout << "Dequeuing items: ";
try {
while (!myQueue.IsEmpty()) {
cout << myQueue.Dequeue() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} catch (const runtime_error& e) {
cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << endl;
}
cout << "Is the queue empty? " << (myQueue.IsEmpty() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
참고문헌
- Nell Dale. (2016). “C++ Plus Data Structues Sixth Edition”. Jones&Bartlett Learning.
- GeeksforGeeks. (2024). “Queue Data Structure”. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-data-structure/.
- 개발자 Miro. (2024). “[자료구조] 스택(Stack)과 큐(Queue)에 대해서 알아보자!”. https://jud00.tistory.com/entry/자료구조-스택Stack과-큐Queue에-대해서-알아보자.
- 맛있는 프로그래머의 일상. (2024). “03 원형 큐(Circular Queue) 자료구조”. https://lktprogrammer.tistory.com/59.
- OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT(Jan 10, 2024). GPT-4. https://chat.openai.com.
- meongju0o0. (2024). “stack.cpp”. https://github.com/meongju0o0/meongju0o0-data-structure.


댓글남기기