[자료구조] 스택(Stack)
스택(Stack)
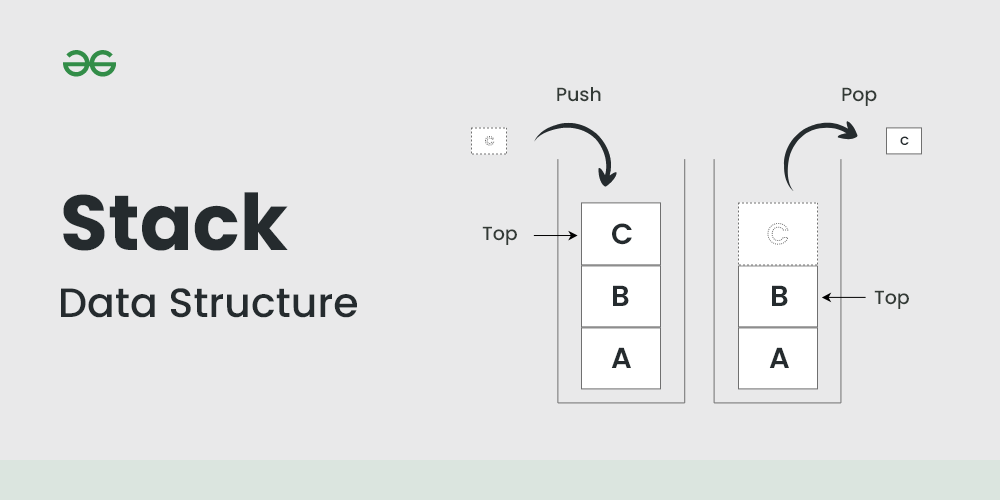
스택(Stack)
- 데이터를 차곡차곡 쌓아 올린 형태의 자료구조
- 데이터가 순서대로 쌓임
- 가장 마지막에 삽입된 자료가 가장 먼저 삭제됨
- LIFO(Last In First Out)형태의 자료구조
- Push
- 스택의 가장 위에 데이터 삽입
- Pop
- 스택의 가장 위의 데이터 삭제
- 스택(Stack)의 사용 사례
- 웹 브라우저 방문기록(뒤로 가기)
- 실행 취소(Undo)
- 역순 문자열 만들기
- 후위 표기법 계산
스택(Stack)에 필요한 Operators
- Constructor
- 스택 객체를 생성하는데 필요한 생성자
- Transformer
- 스택의 상태 (들어있는 아이템의 값 등)을 변환하는 변환자
- Observer
- 스택의 아이템이나 길이 등의 정보에 접근하는 관측자
Stack Operators(Array Based)
- Transformers
- Push
- Pop
- Observers
- IsEmpty
- IsFull
- Top
Source Code
Preprocessing
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_ITEMS 50
#define FULL_STACK "stack is full"
#define EMPTY_STACK "stack is empty"
typedef int ItemType;
class StackType;
Class Definition
class StackType {
public:
StackType();
[[nodiscard]] bool IsFull() const; // 스택이 가득 차있는지 확인
[[nodiscard]] bool IsEmpty() const; // 스택이 비어있는지 확인
[[nodiscard]] ItemType Top() const; // 스택 상단의 아이템 확인
void Push(ItemType newItem); // 스택 상단에 아이템 삽입
ItemType Pop(); // 스택 상단의 아이템 삭제
private:
int top;
ItemType items[MAX_ITEMS]{};
};
Class Constructor
StackType::StackType() {
top = -1;
}
Class Transformer
void StackType::Push(ItemType newItem) {
if(IsFull()) {
throw runtime_error(FULL_STACK);
}
items[++top] = newItem;
}
ItemType StackType::Pop() {
if(IsEmpty()) {
throw runtime_error(EMPTY_STACK);
}
return items[top--];
}
Class Observer
bool StackType::IsEmpty() const {
return top == -1;
}
bool StackType::IsFull() const {
return top == (MAX_ITEMS - 1);
}
ItemType StackType::Top() {
if(IsEmpty()) {
throw runtime_error(EMPTY_STACK);
}
return items[top];
}
Main Function
int main() {
StackType myStack;
// 푸시
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
cout << "Pushing " << i << " onto the stack." << endl;
myStack.Push(i);
}
} catch (const runtime_error& e) {
cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << endl;
}
// 탑
try {
cout << "Top item of the stack: " << myStack.Top() << endl;
} catch (const runtime_error& e) {
cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << endl;
}
// 팝
cout << "Popping items: ";
try {
while (!myStack.IsEmpty()) {
cout << myStack.Pop() << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} catch (const runtime_error& e) {
cout << "Exception caught: " << e.what() << endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Result
Pushing 1 onto the stack.
Pushing 2 onto the stack.
Pushing 3 onto the stack.
Pushing 4 onto the stack.
Pushing 5 onto the stack.
Top item of the stack: 5
Popping items: 5 4 3 2 1
참고문헌
- Nell Dale. (2016). “C++ Plus Data Structues Sixth Edition”. Jones&Bartlett Learning.
- GeeksforGeeks. (2024). “Stack Data Structure”. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stack-data-structure/.
- 개발자 Miro. (2024). “[자료구조] 스택(Stack)과 큐(Queue)에 대해서 알아보자!”. https://jud00.tistory.com/entry/자료구조-스택Stack과-큐Queue에-대해서-알아보자.
- OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT(Jan 10, 2024). GPT-4. https://chat.openai.com.
- meongju0o0. (2024). “stack.cpp”. https://github.com/meongju0o0/meongju0o0-data-structure.


댓글남기기