LSA
Latent Semantic Analysis, LSA
Fundamental Concept
- It is used in the field of data information retreival
- By using LSA, we can see the latent relevance of words from a large amount of document data.
Algorithm
- Convert the sentence below to matrix X.
- 자동차로 회사에 출근했다.
- 차로 출근했다.
- 레스토랑에서 햄버거를 먹는다.
- 레스토랑에서 파스타를 먹는다.
| 문장1 | 문장2 | 문장3 | 문장4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 자동차 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 회사 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 출근 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 차 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 레스토랑 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 햄버거 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 먹다 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 파스타 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
- Decompose the matrix X.
- The matrix X, which is an 8X4 matrix, is represented by the product of the 8X4 matrix U, the 4X4 matrix D, and the 4X4 matrix V^T.
- Matrix U: Matrix with transformation information of characteristics made of words
- Matrix D: Matrix with information importance
- Matrix V: Matrix with word features and document conversion information
- The matrix X, which is an 8X4 matrix, is represented by the product of the 8X4 matrix U, the 4X4 matrix D, and the 4X4 matrix V^T.

- The matrix D is a diagonal matrix. Diagonal elements list values in order of greater importance of information.
- Therefore, if we reduce the dimension to three matrices, we should look at D carefully.
- Since the original data has four features, let’s say that the dimension is reduced to two features.
- From the diagonal element values of a matrix D with four features, choose two elements of greater importance to form a 2X2 diagonal matrix.
- The other two matrices are also changed to correspond to the elements selected in D.
- The matrix U deletes the entire elements of the third and fourth columns and replaces them with an 8X2 matrix.
- The matrix V^T deletes all elements of the third and fourth rows to form a 2X4 matrix.
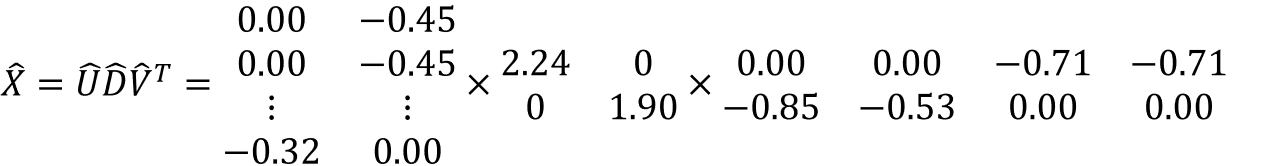
- Table of 2 features divided by latent variables ||A|B| |:–|:–:|:–:| |자동차|0.00|0.85| |회사|0.00|0.85| |출근|0.00|1.38| |차|0.00|0.53| |레스토랑|1.41|0.00| |햄버거|0.71|0.00| |먹다|1.41|0.00| |파스타|0.71|0.00|
from sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD
data = [[1,0,0,0],
[1,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0],
[0,1,0,0],
[0,0,1,1],
[0,0,1,0],
[0,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,1]]
n_components = 2
model = TruncatedSVD(n_components=n_components)
model.fit(data)
print(model.transform(data))
print(model.explained_variance_ratio_)
print(sum(model.explained_variance_ratio_))
[[ 0.00000000e+00 8.50650808e-01]
[ 0.00000000e+00 8.50650808e-01]
[-2.71947991e-16 1.37638192e+00]
[-2.71947991e-16 5.25731112e-01]
[ 1.41421356e+00 2.02192262e-16]
[ 7.07106781e-01 0.00000000e+00]
[ 1.41421356e+00 2.02192262e-16]
[ 7.07106781e-01 2.02192262e-16]]
[0.38596491 0.27999429]
0.6659592065833294
Points to note
- It is difficult to properly explain the relevance of words with the converted matrix. If each dimension is orthogonal or the matrix element is negative, it is difficult to properly explain the relevance.
- The calculation can take a very long time.
참고문헌
- 秋庭伸也 et al. 머신러닝 도감 : 그림으로 공부하는 머신러닝 알고리즘 17 / 아키바 신야, 스기야마 아세이, 데라다 마나부 [공] 지음 ; 이중민 옮김, 2019.


댓글남기기