Neural Network
Neural Network
Fundamental Concept
- A neural network is a model that learns complex decision lines by defining a hidden layer between the input layer and the output layer.
- It can be applied to both regression and classification, but it is mainly applied to classification problems.
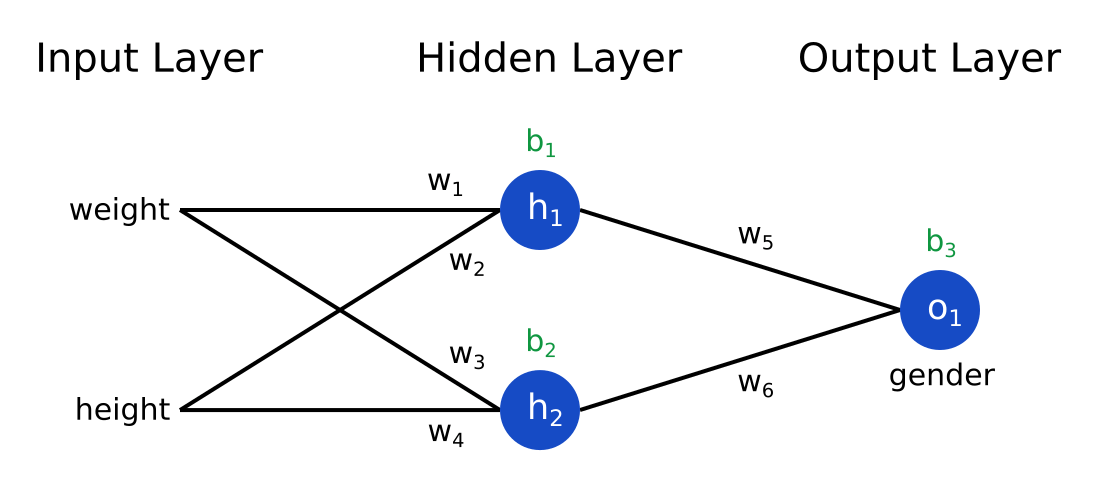
- The above figure is a neural network in which the input layer is 2D, the hidden layer is 2D, and the output layer is 1D.
- After applying a neural network to classifying NIST, a dataset composed of cursive letters, we will check the classification results.
- NIST has 10 cursive letters ranging from 0 to 9.
- The input layer represents the input cursive numeric image itself.
- The pixel values of each point are stored in a 1D column vector.
- The hidden layer calculates a value received from the input layer with a nonlinear function such as a sigmoid function.
- The larger the hyperparameters, the more complex decision lines are learned, but overfitting is likely to occur.
- The output layer also calculates the value received from the hidden layer as a nonlinear function.
- The output layer outputs 10 probabilities that the input cursive numerical image belongs to one of 0 to 9.
Algorithm
fault perceptron
- A fault perceptron is a model that identifies data by applying a nonlinear function to a result obtained by multiplying a feature by a weight.
- For example, if feature is 2D, input feature is (x_1, x_2).
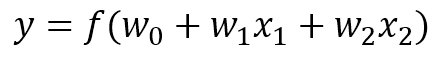
- we call w_1, w_2 as a weight, w_0 as a bias.
- Weight and bias are parameters used for learning.
- non-linear function f is called activation function
- The probability y is calculated using the sum of the weights and features. In this case, the activation function uses a sigmoid function or the like.
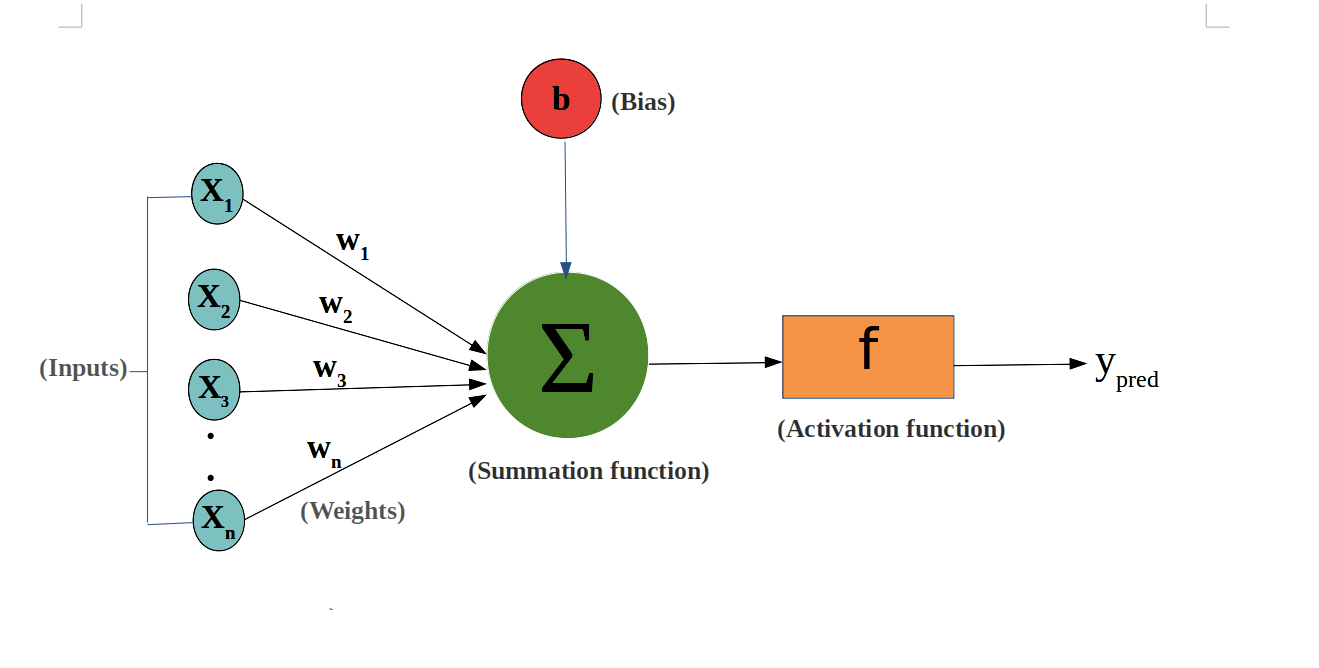
-
It also simply shows only the input and output parts.
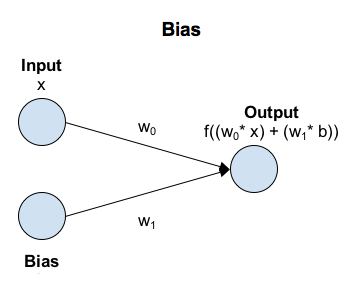
- Fault perceptrons have similar characteristics to logistic regression.
- If activation function f is only sigmoid function, fault perceptron is same as logistic regression.
neural network
- A neural network is a model that defines several fault perceptrons to represent complex decision line.
- fault perceptron can’t learn decision line correctly.
- Set a hidden layer between the input and output.
- Set the decision to make the final decision by combining the output results of the two layers.
Sample Code
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
data = load_digits()
X = data.images.reshape(len(data.images), -1)
y = data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.3)
model = MLPClassifier(hidden_layer_sizes=(16, ), max_iter = 1000)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
accuracy_score(y_pred, y_test)
0.9407407407407408
early stopping
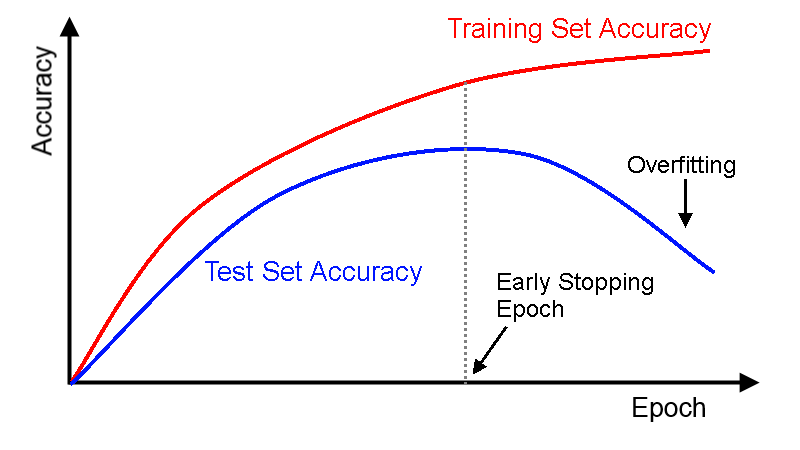
- Some of the learning data is further divided into evaluation data used during learning.
- It stores evaluation indicators such as loss in order with evaluation data used during learning so that the degree of learning progress can be known.
- If there are signs of overfitting during learning, the learning is terminated in the middle.
참고문헌
- 秋庭伸也 et al. 머신러닝 도감 : 그림으로 공부하는 머신러닝 알고리즘 17 / 아키바 신야, 스기야마 아세이, 데라다 마나부 [공] 지음 ; 이중민 옮김, 2019.


댓글남기기