Random Forest
Random Forest
Fundamental Concept
- Random forest is a method of combining various models to create a high-performance model.
- It can be used for both regression and classification problems.
-
Similar algorithms include gradient boosting.
- Random forest uses multiple models called decision trees to increase accuracy than using a single decision tree.
- Random forest is used for both classification and regression problems, but this section exemplifies the classification problem.
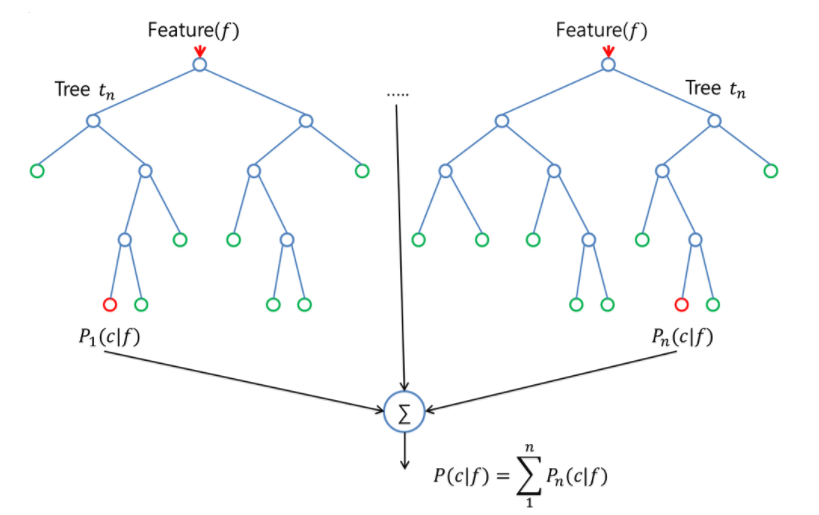
- The most predictive results are obtained as the final classification result by collecting the predictive results from each decision tree.
- Random forest should be different for each decision tree.
Algorithm
Decision Tree
- When dividing learning data, impurity, which represents the imbalance of data, is digitized and used.
- The decision tree divides the data so that the impurity is reduced.
- If there are many of the same labels in the divided group, the impurity decreases.
-
If there are many other labels in the divided group, the impurity increases.
- There are several indicators of impurities, where Gini index will be used.
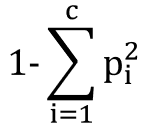
- In this case, c is the number of labels and p_i is the number of labels divided by the number of data.
- The Gini coefficient and the weighted average using it are calculated according to the method of dividing the data.
- Calculate all features of one area and the impurity of the object to be divided
- Divide areas to minimize impurities.
- After dividing, repeat 1~2 steps in each area.
random forest
- Bootstrap: A method of “increasing” learning data by performing random recovery extractions from learning data several times. In one learning data, several learning data with different contents are generated and the learning data placed in each decision tree is different.
- Certain optional choices: Choose and use only a few features randomly when learning the decision tree with bootstrap learning data.
- Random forest learns to have different classification results using the above method.
Sample Code
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
data = load_wine()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data.data, data.target, test_size = 0.3)
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators = 10)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
accuracy_score(y_pred, y_test)
0.9444444444444444
importance of feature
- Feature of high importance are expected to significantly reduce impurities by using them as criteria for dividing areas.
- The feature of low importance is that it is difficult to reduce impurities even when used as a criterion for dividing areas.
- In this way, attention should be paid to the importance of features and unnecessary features should be reduced.
참고문헌
- 秋庭伸也 et al. 머신러닝 도감 : 그림으로 공부하는 머신러닝 알고리즘 17 / 아키바 신야, 스기야마 아세이, 데라다 마나부 [공] 지음 ; 이중민 옮김, 2019.


댓글남기기