HNSW
Hierarchical Navigable Small World
About Paper
- 제목: Efficient and robust approximate nearest neighbor search using Hierarchical Navigable Small World grpahs
- 저널: IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence. 2018.
- 저자: Yu. A. Malkov, D. A. Yashunin
Preliminary Knowledge
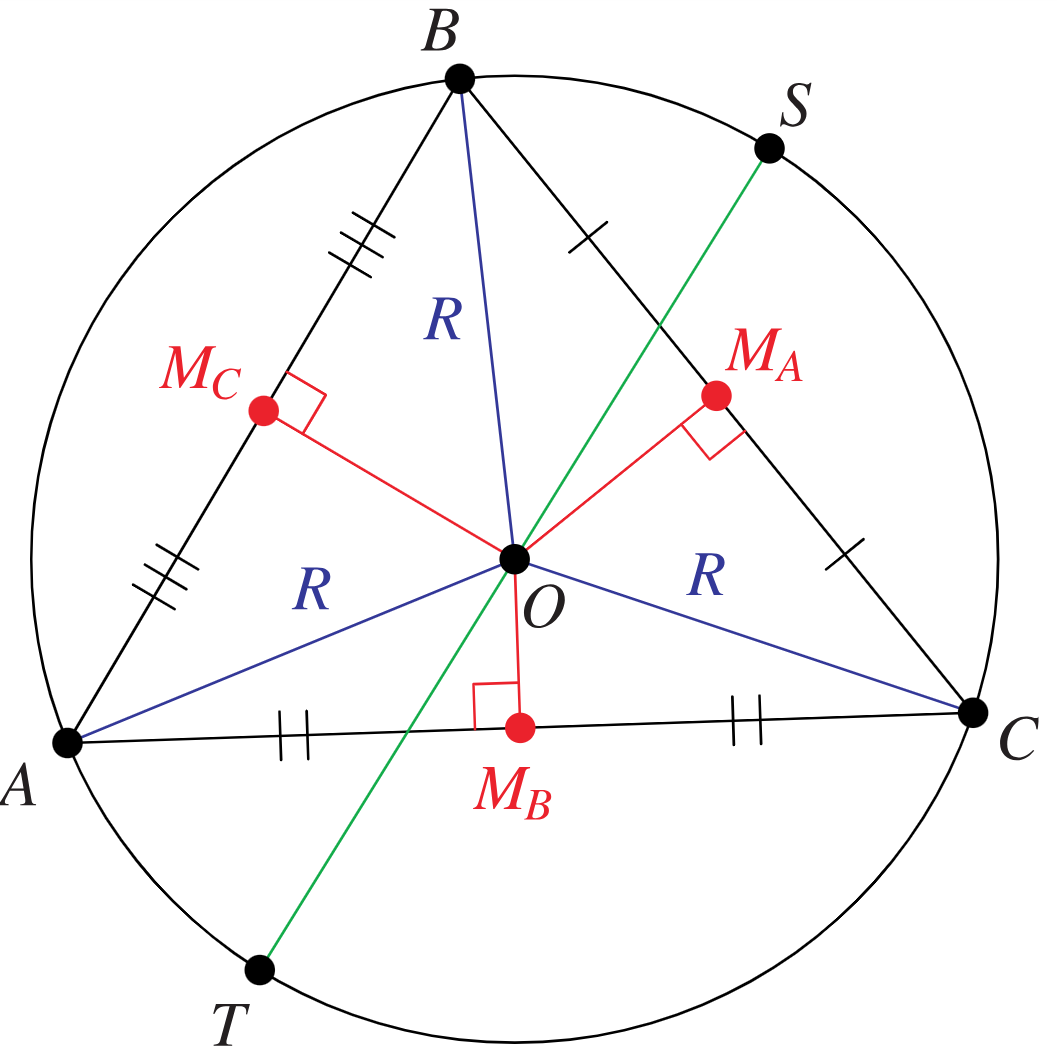
Delaunay triangulation(들로네 삼각분할)
- 들로네 삼각분할
- 평면 위 점들을 삼각형으로 연결하여 공간을 분할할 때, 이 삼각형들의 내각의 최소값이 최대가 되도록 하는 분할
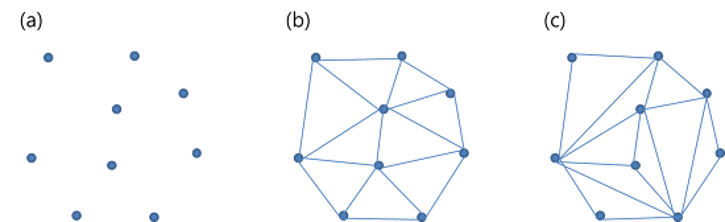
- 들로네 삼각분할은 (c)가 아닌 (b)와 같은 모양이 나오게끔 그래프를 구축하는 알고리즘
- 위 들로네 삼각분할의 가장 중용한 특징은 아래와 같음
- 어떤 삼각형의 외접원도 그 삼각형의 세 꼭지점을 제외한 다른 어떤 점도 포함하지 않는다
- 이를 empty circumcircle property라고 함
- kNN Index 중 Delaunay Graph가 한때 사용되곤 했음
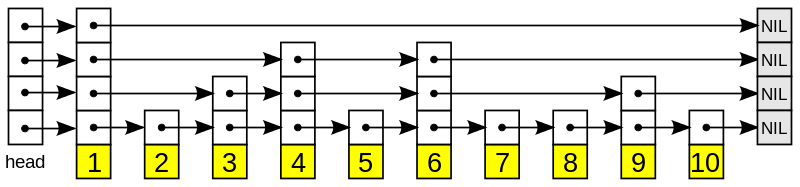
probabilistic skip list
- linked list를 개선한 자료구조
- linked list의 가장 큰 단점이 random access가 불가능하다는 것이다
- 위 단점으로 인해 Sorted List마저 탐색 시간복잡도가 $O(n)$이 된다
- 위 단점을 극복하고자 일부 노드는 한번에 여러 칸을 건너뛸 수 있도록 설계(skip)
- 이때, 노드의 포인터 개수는 확률적으로 정해짐(probabilistic)
Small World
- Regular Graph에서 일부 에지를 삭제한 후 무작위로 연결한 그래프
-
Regular Graph에 비해 특정 지점으로 이동하는데 필요한 distance 감소
- Algorithm
- 평균 차수가 2K인 N개 노드를 갖는 링 모양 격자 생성
- 각 노드는 양쪽으로 K개의 최근접 이웃 노드에 연결
- 그래프의 각 간선에 대해 확룔 $\beta$ 를 사용하여 타깃 노드를 재연결
- 재연결된 간선은 중복 간선이거나 자가 루프일 수 없음
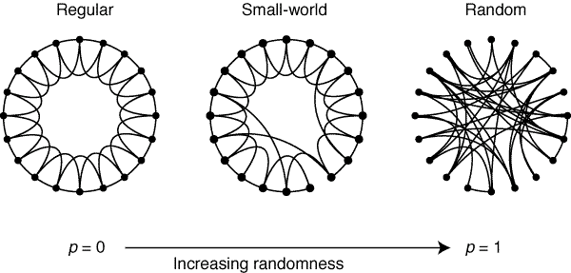
- 이점
- regular graph에서 두 노드를 선택했을 때, 이동 거리(즉, 그래프 탐색 횟수)에 비해 small world graph는 확연히 줄어듬
- 일부 노드를 재연결하여 먼 거리의 노드를 연결하였기 때문
Navigable Small World
Navigable Small World Introduction
- Nearest Neighbor Index 구축 시, graph를 생성하는 이유
- 근접하는 이웃 기리 에지를 생성하여 query point의 neighbor 만을 탐색
- 그래프 이동 경로를 따라 최근접 이웃을 탐색하므로 탐색 범위 축소
- 그래프 이동 경로의 1-hop neighbor들 만을 탐색
- naive idea로 최근접 이웃끼리 에지를 생성한다고 해보자
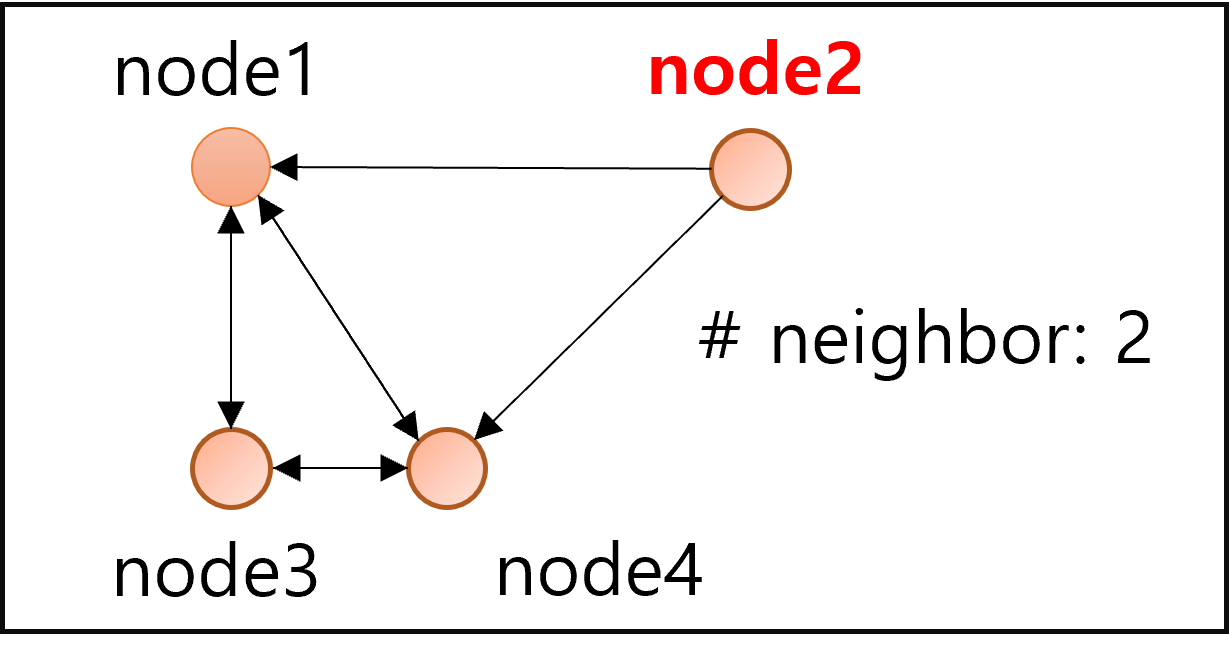
- 위 그림과 같이 탐색이 불가능한 노드 발생: node2
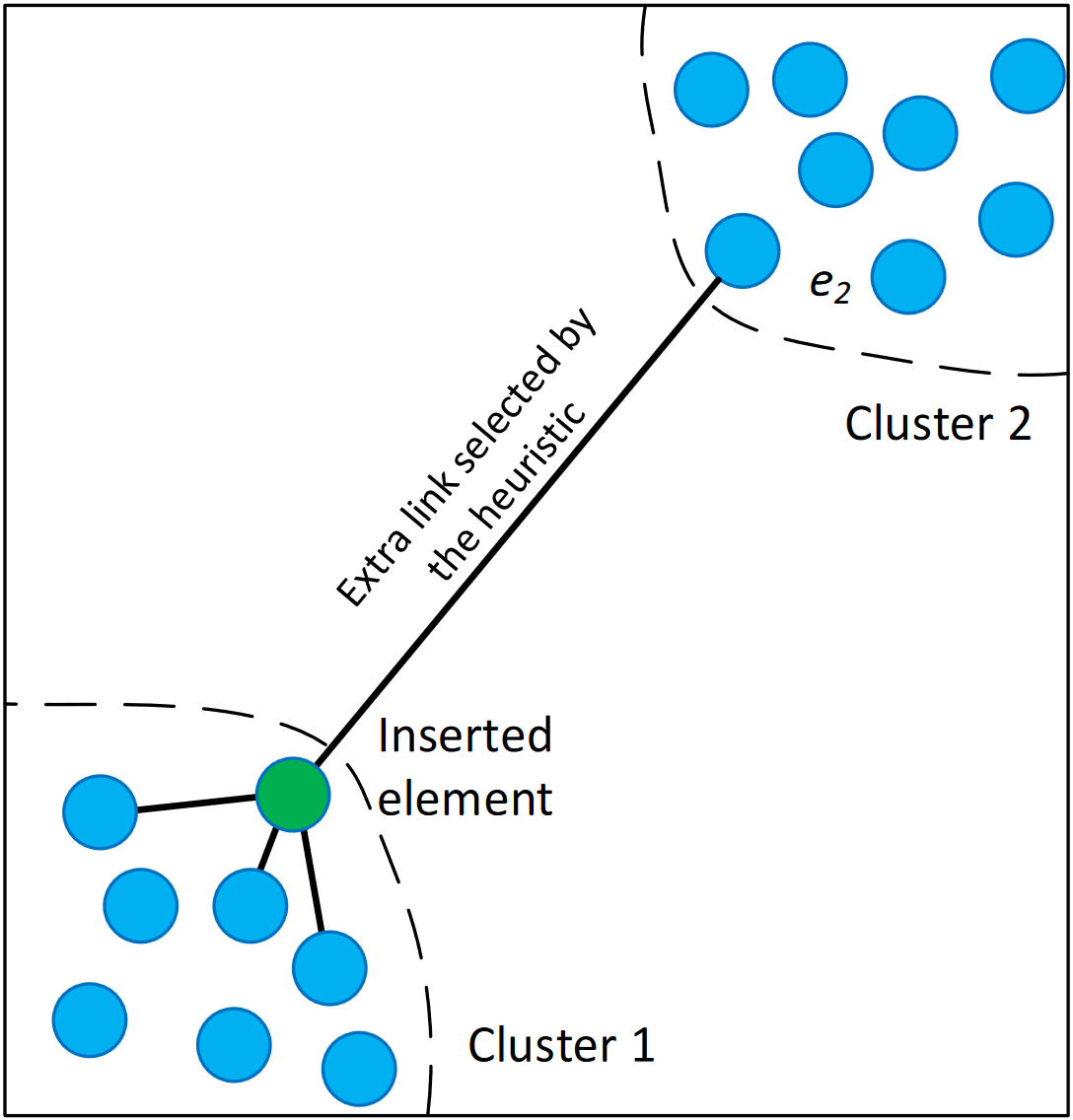
- 해당 논문의 NSW Graph는 bidirectional edge를 사용하나, bidirectional edge여도 아래 그림의 경우 탐색이 불가능한 노드(혹은 클러스터) 발생
-
즉, 클러스터 간에 이동할 수 있는 에지가 생성되지 않음
- 이에 본 논문에서는 heuristic algorithm을 사용하라고 제안
Navigable Small World Algorithm
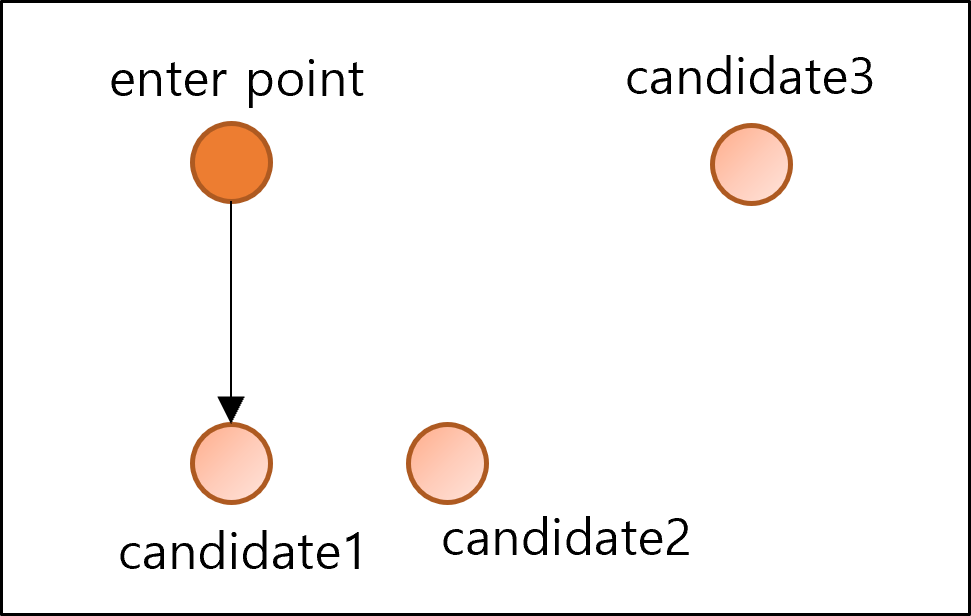
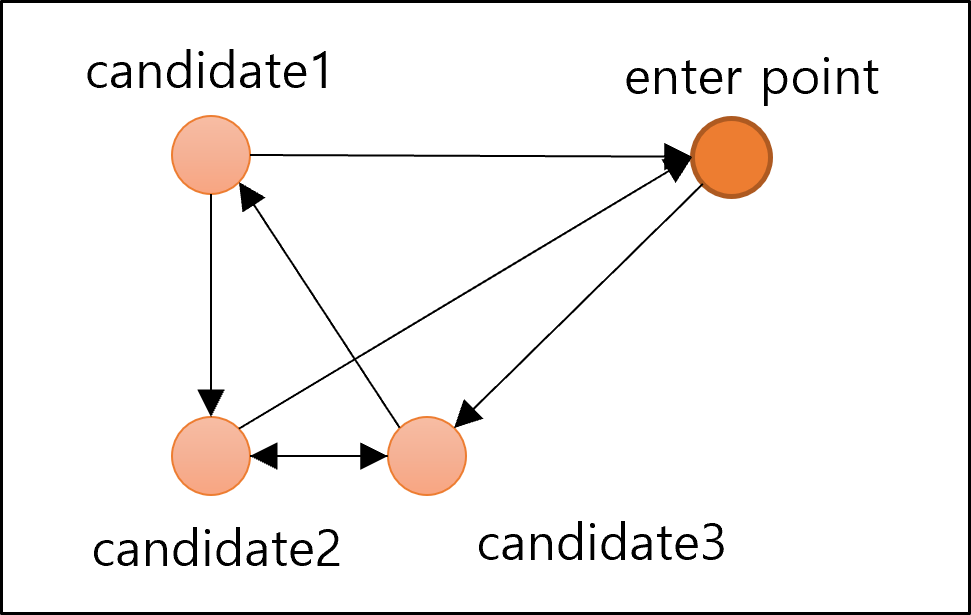
- 처음에는 가장 가까운 이웃을 선택하여 에지 생성
- 새로 연결될 candidate는 기존에 연결된 candidate와 새로 연결될 candidate사이의 거리보다 멀어야 함
- 새로 연결될 candidate: candidate2, candidate3
- 기존에 연결된 candidate: candidate1
- 즉, candidate1과 candidate2사이의 거리는 enterpoint와 candidate2 사이의 거리보다 가까우므로 연결이 되지 않음
- 한편, candidate1와 candidate3사이의 거리는 enterpoint와 candidate3 사이의 거리보다 멀으므로 연결이 가능함
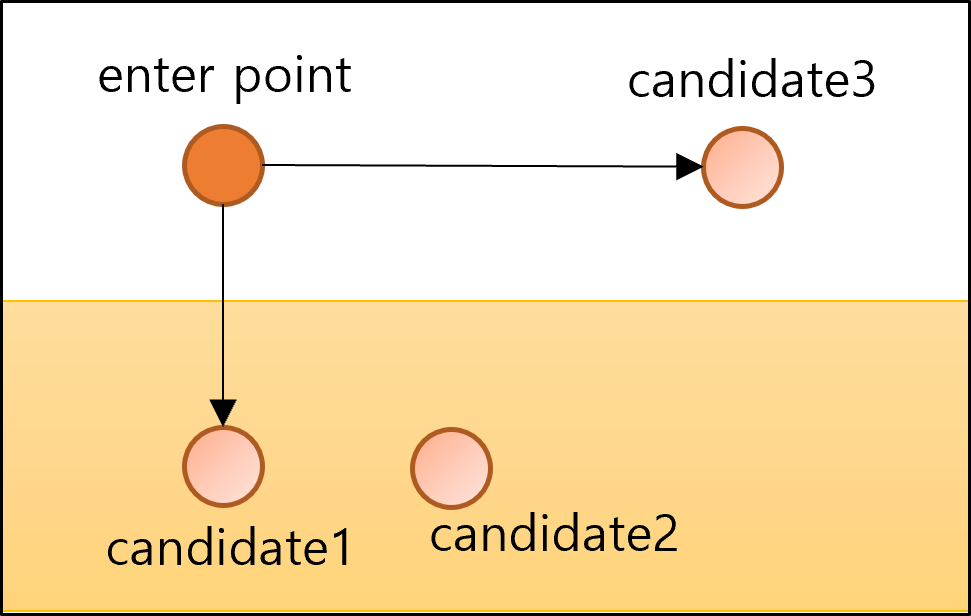
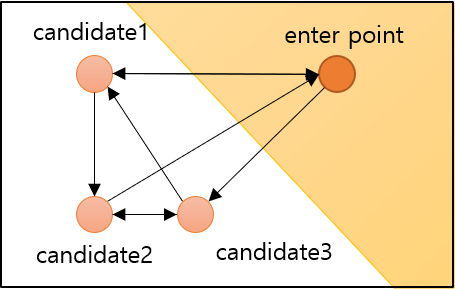
- 위 그림에서 노란색 배경으로 처리된 부분이 노드를 추가할 수 없는 부분
- 반대로 하얀색 배경은 노드를 추가할 수 있는 부분
- enterpoint를 변경하여 위 두 과정 반복
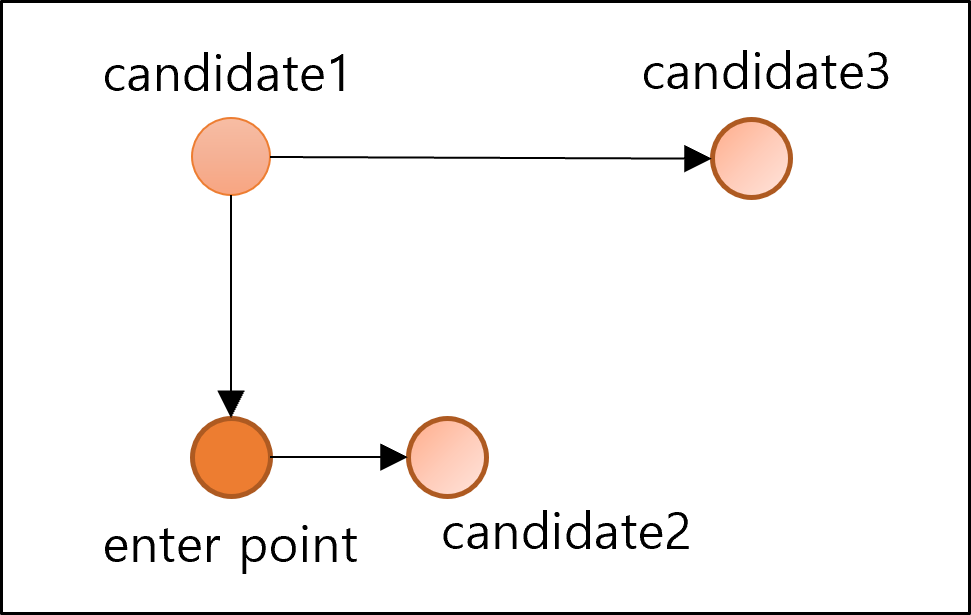
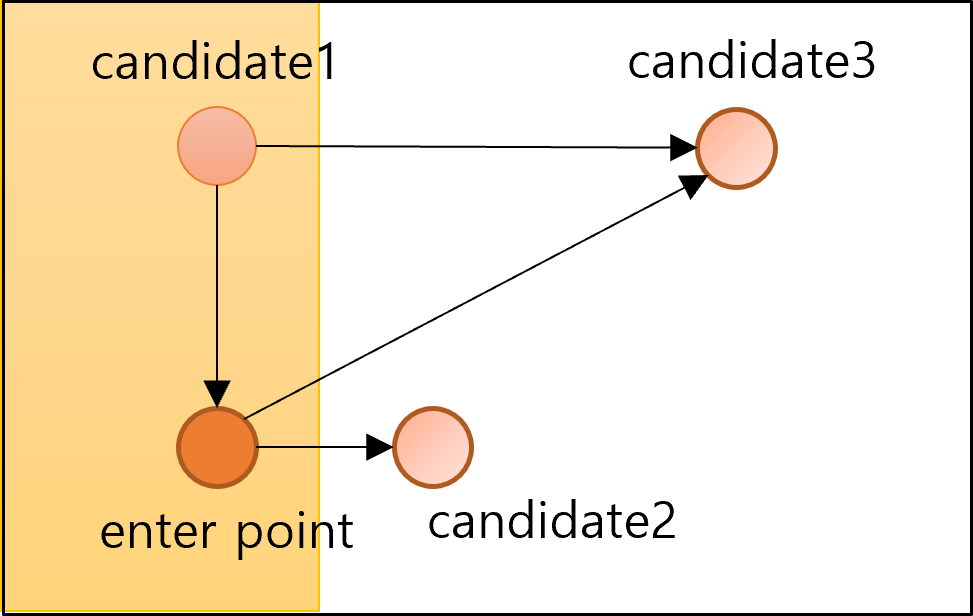
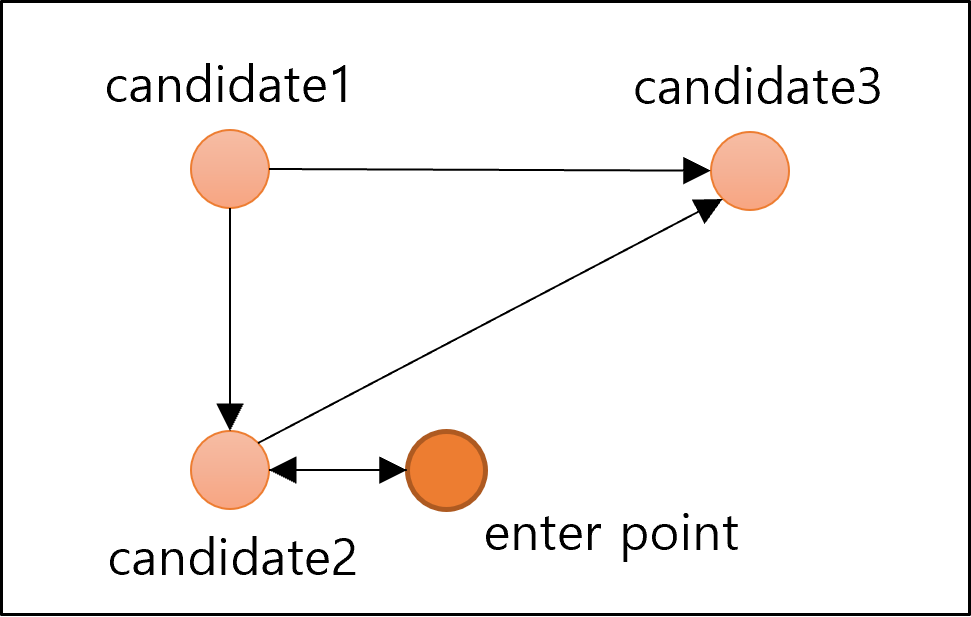
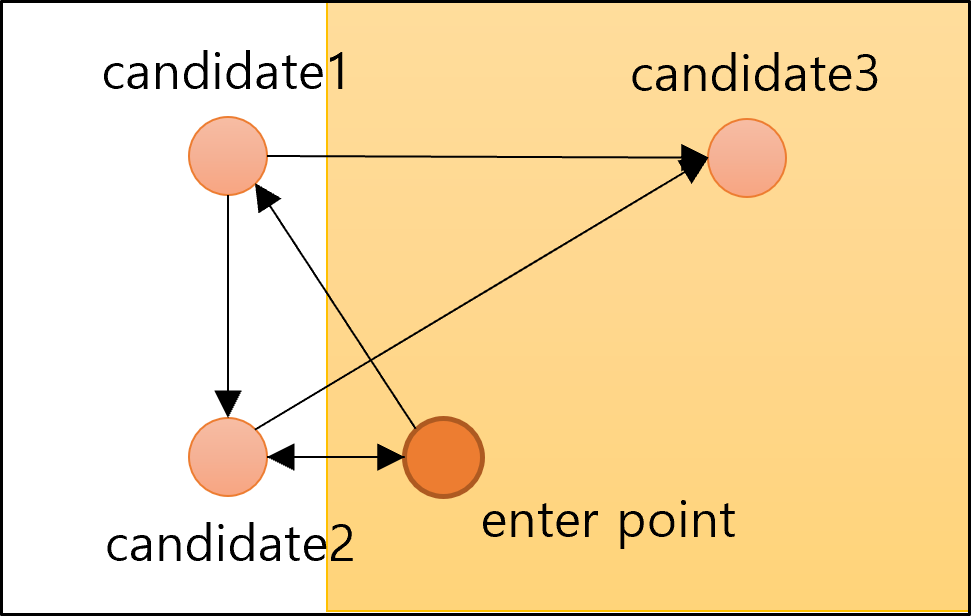
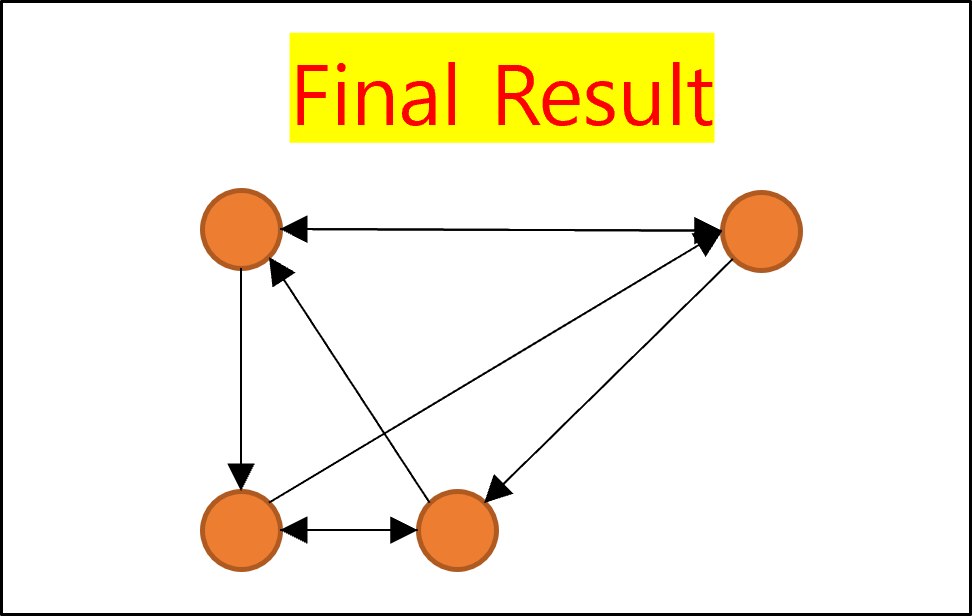
Navigable Small World Graph
- 위 과정은 Regular Graph를 형성하는 과정
- 위 그래프에서 일부 에지를 재연결함으로서 Navigable Small World Graph가 완성됨
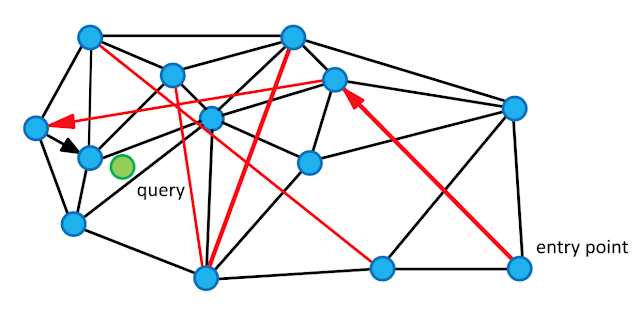
- 빨간색 에지가 재연결된 에지
-
화살표가 있는 에지가 탐색 경로
- Navgable Small World Graph의 가장 큰 단점은 local minimum에 빠지는 경우가 많다는 것이다.
- 즉, 비록 같은 Approximate Nearest Neighbor Algorithm이지만 더 정확한 Nearest Neighbor를 찾고싶은 것이 Hierarchical Navigable Small World의 등장 배경이다.
Hierarchical Navigable Small World
Motivation
- NSW Graph의 local minimum 문제 해결
- probabilistic skip list의 아이디어에서 창안해 확률적으로 일부 노드를 샘플링하여 여러 계층의 그래프를 구축
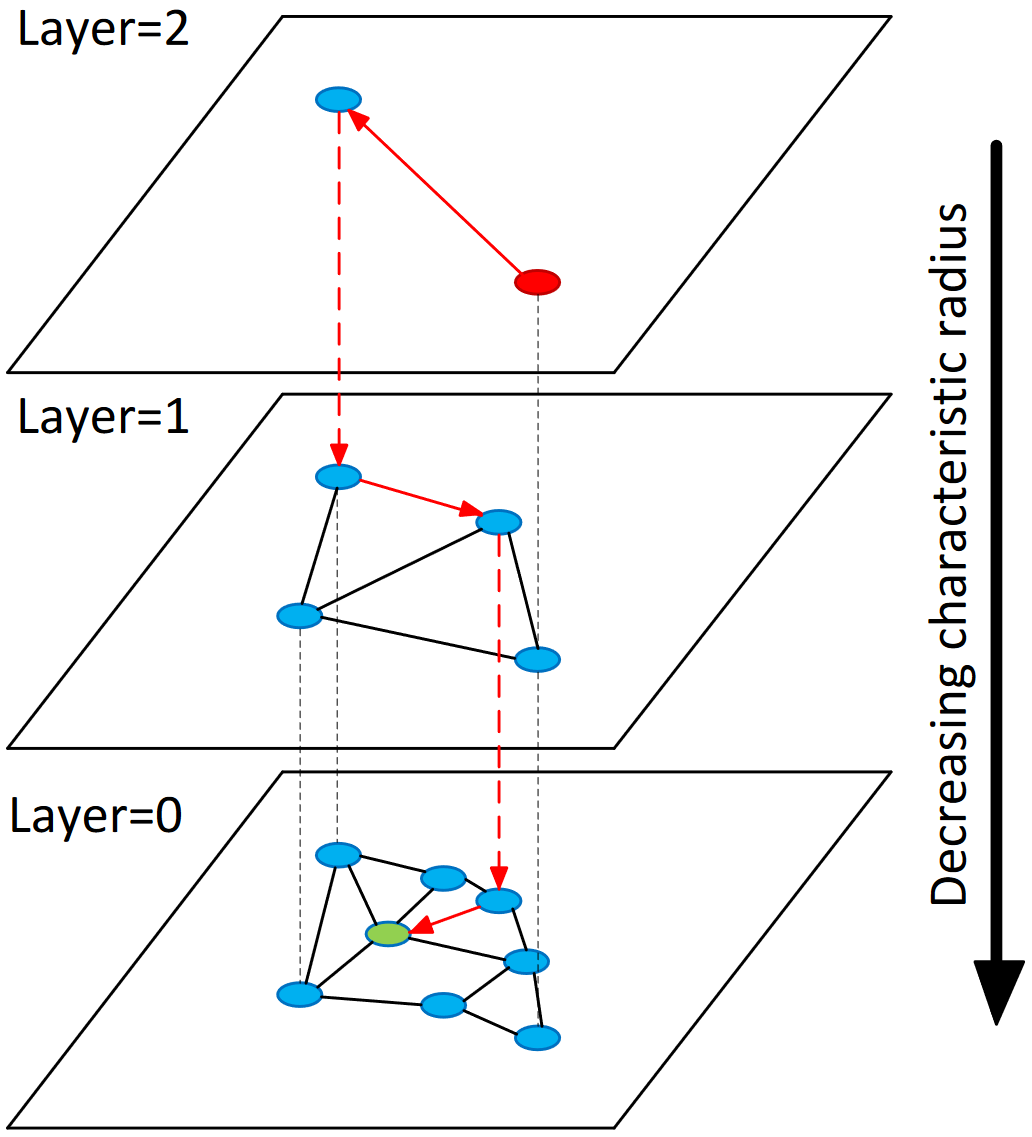
Introduction
- 계층적으로 NSW를 구축하여 Nearest Neighbor 탐색
- NSW 그래프에서 삭제되는 에지가 없으므로 ANN Search의 Recall 보존
- 상위 계층에서 한번에 많이 이동하여 Time Efficiency 개선
- 여러 계층에 걸쳐 NSW를 구축
- 상위 계층에서는 entry point에서 한번에 멀리 이동하면서 Nearest Neighbor 탐색
- 하위 계층에서는 정확도를 보장하기 위해 조금씩 이동하면서 Nearest Neighbor 탐색
- 상위 계층의 노드는 무작위로 추출
- 추출된 노드를 활용하여 위 NSW Graph 구축
HNSW Search Algorithm
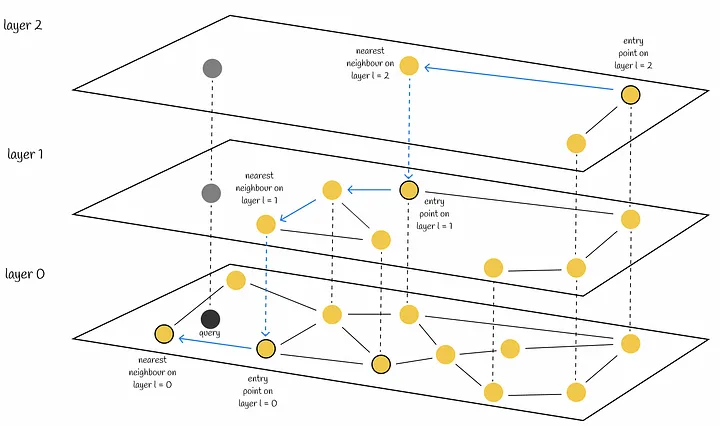
- 최상위 계층의 entry point에서 가장 가까운 neighbor를 Greedy Best-First Search Algorithm(Greedy BFS)으로 탐색
- 상위 계층의 nearest neighbor를 entry point로 설정하여 Greedy BFS 탐색
- 최하위 계층에서 nearest neighbor를 k개 선택할 때까지 반복
K–NN–SEARCH($hnsw$, $q$, $K$, $ef$)
- parameters
- multilayer graph: $hnsw$
- query element: $q$
- number of nearest neighbors to return: $K$
- size of dynamic candidate list: $ef$
- initialize
- $ef$개의 nearest elements 저장: $W$
- enter points: $ep$
- $ep$의 계층 번호: $L$

- $ef$는 무엇인가?
- $ef$ 만큼의 nearest neighbor를 SEARCH-LAYER를 통해 탐색, SEARCH-LAYER는 $ef$개의 nearest neighbor를 반환. 반환된 $ef$개의 nearest neighbor를 $W$에 저장한 뒤 $W$에서 최근접 이웃 $K$개를 선택하여 반환
SEARCH–LAYER($q$, $ep$, $ef$, $l_c$)
- parameters
- query element: $q$
- enter points: $ep$
- number of nearest to $q$ elements to return: $ef$
- layer number: $l_c$
- initialize
- 방문한 노드 저장: $v$
- 후보 노드 저장: $C$
- 최종적으로 반환할 nearest elements list: $W$, (최대 길이: $ef$)

HNSW Insert Algorithm
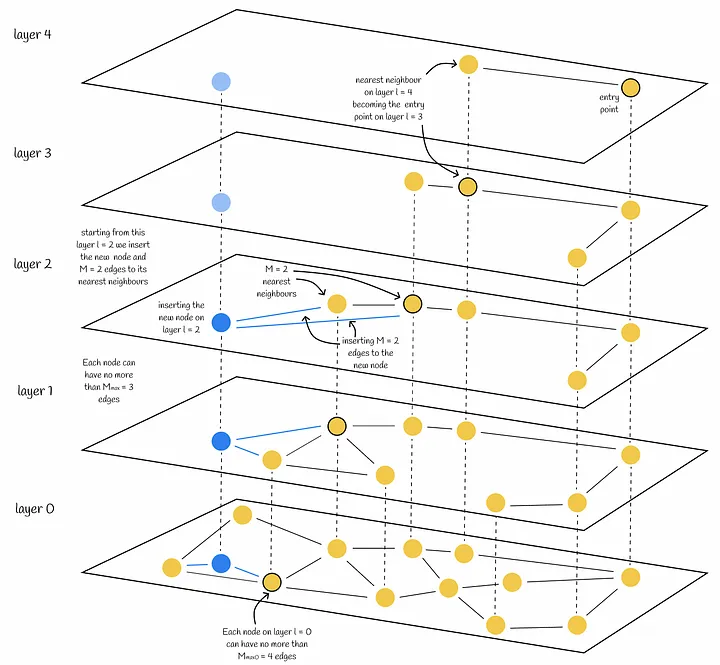
- Insert 시에 고려해야 할 사항
- 어느 레이어에 삽입할 것인가?
- 해당 레이어에서 에지를 생성할 candidate node는 무엇인가?
- 어느 레이어에 삽입할 것인가?
- 삽입될 노드의 최상위 레이어를 $l$이라 하자
- $l=\left\lfloor{-ln(uniform(0, 1) \cdot m_L)}\right\rfloor$
- $m_L=1/ln(M)$
- $M$: 노드 당 최소 neighbor 수
- $m_L$을 지나치게 크게 하면 하위 레이어 수가 너무 많아져 탐색에 방해, linear-search에 근사
- $m_L$을 지나치게 작게 하면 레이어 내 그래프 탐색 횟수가 지나치게 많아짐
- 즉, $m_L$은 레벨 생성의 정규화 요소
- 해당 레이어에서 에지를 생성할 candidate node는 무엇인가?
- 최상위 계층에서 greedy BFS로 Insert Point의 최근접 이웃을 탐색
- 상위 계층의 nearest neighbor은 하위 계층의 entry point로 사용
- 계산된 삽입할 레이어 $l$에 도착하면 $efConstruction$ 만큼의 neighbor를 탐색하고 $M$만큼 에지 추가
- $efConstruction$: size of dynamic candidate list
- 하위 레이어($l-1$, $l-2$, $…$, $0$)에서도 같은 작업 반복
INSERT($hnsw$, $q$, $M$, $M_{max}$, $efConstruction$, $m_L$)
- parameters
- 추가할 벡터: $q$
- 연결 할 이웃 수: $M$
- 연결 가능한 최대 이웃 수: $M_{max}$
- 에지 추가 시에 고려할 최근접 이웃 후보 리스트 사이즈: $efConstruction$
- 레벨 생성 정규화 요소: $m_L$

SELECT–NEIGHBORS–HEURISTIC($q$, $C$, $M$, $l_c$, $extendCandidates$, $keepPrunedConnections$)
- parameters
- 추가할 벡터: $q$
- 후보 벡터 리스트: $C$
- 연결 할 이웃 수: $M$
- candidate의 neighbor들도 후보 벡터 리스트 $C$에 추가할 것인지: $extendCandidates$
- 버려진 candidate를 $M$만큼 연결하지 못하였을 때 연결할 것인지: $keepPrunedConnections$

Experiments
- HNSW Index는 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝이 필요한 알고리즘
- $M$: 노드 당 최소 neighbor 수
- $M$이 클수록 인덱스 빌드 시간 및 벡터 질의 시간 증가
- $M_{max}$의 경우, $M_{max}=2*M$으로 고정
- $efConstruction$: 인덱스 빌드 시 이웃 노드를 저장하는 동적 큐의 크기
- $efConstruction$이 클수록 인덱스 빌드 시간 증가
- 질의 시간에 직접적인 영향은 없음
- $ef$: 질의 시 방문한 이웃 노드를 저장해 놓은 동적 큐
- 해당 값 만큼 노드를 탐색 후, 탐색된 노드에서 $K$개의 nearest neighbor 반환
- 검색 개수인 $K$보다 크거나 같아야함
- 질의 시간에 관여
- 빌드 시간에는 영향이 없음
- $M$: 노드 당 최소 neighbor 수
$M$에 따른 재현율(recall)과 응답시간 및 빌드시간 간의 trade-off
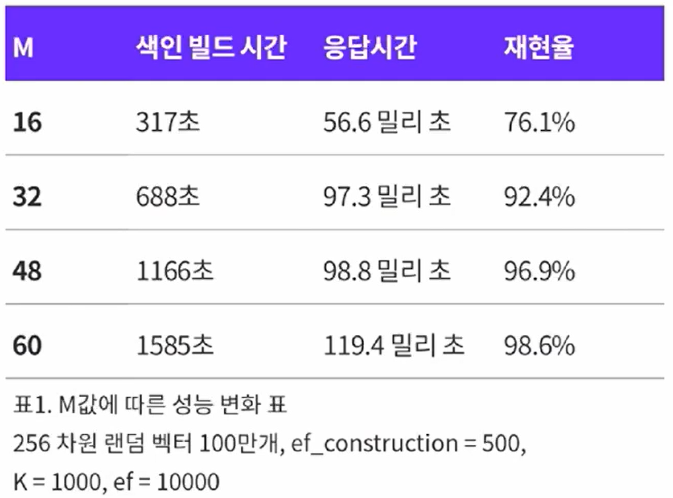
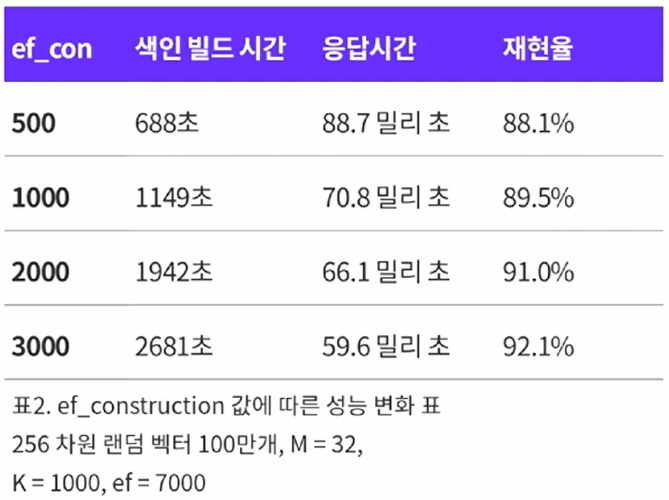
$efConstruction$에 따른 재현율(recall)과 빌드시간 간의 trade-off
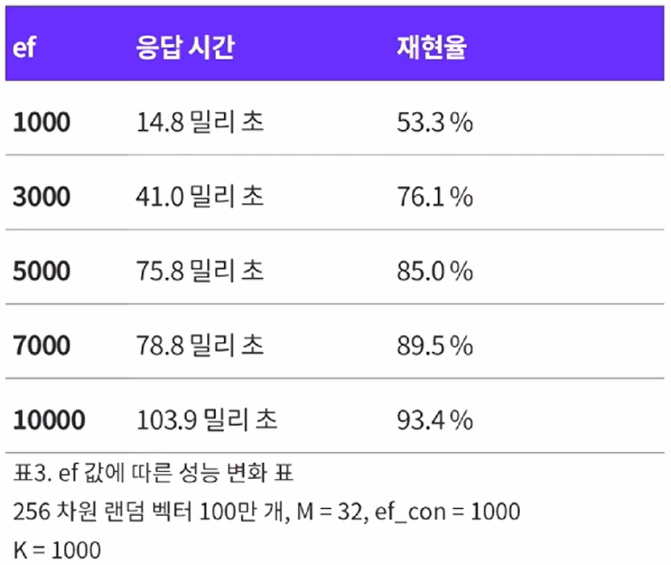
$ef$에 따른 재현율(recall)과 응답시간 간의 trade-off
데이터 경향성에 따른 응담 속도 및 재현율(recall)
- 앞선 실험은 uniform random한 256차원 벡터로 수행
- 그러나, 실세계의 벡터는 임베딩들이 클러스터를 이루는 경우가 훨씬 더 많음
- 아래 그림은 이에 따른 실험 결과
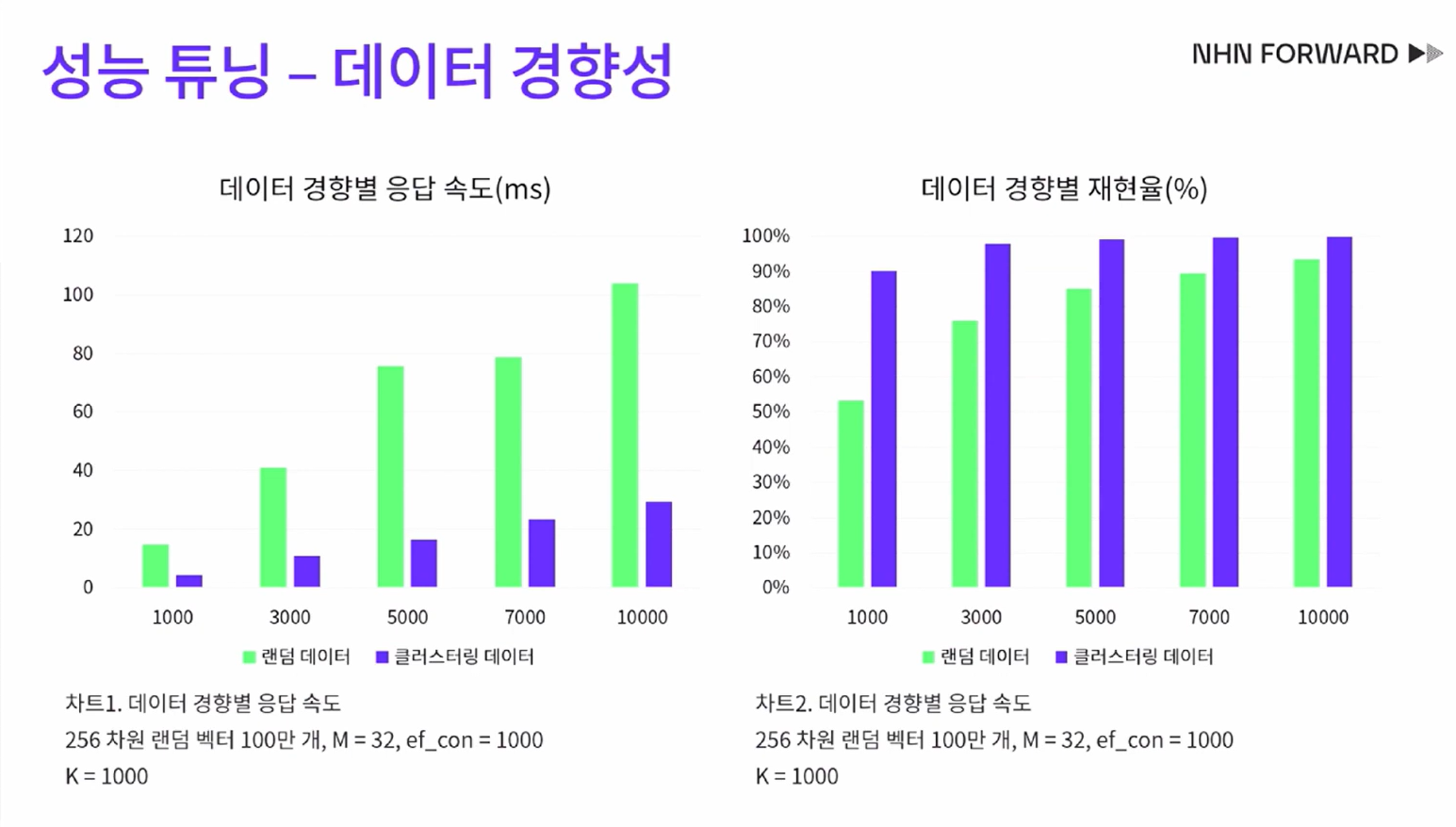
출처: NHN Cloud. NHN Cloud 로그플랫폼 개발팀 권성재. 2023.01.04. “[NHN FORWARD 22] 대충? 거의 정확하다! 벡터 검색 엔진에 ANN HNSW 알고리즘 도입기 (feat. SWIG Golang)”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hCqF4tDPNBw&t=1050s
파라미터 접근 전략
- 빌드 시, $M$과 $efConstruction$ 값을 조정하면서 재현율을 올림
- $M$은 색인 크기와 빌드 시간에 직접적 영향
- $efConstruction$은 빌드 시간에 영향
- 검색 시, $ef$값을 조정하면서 응답 시간과 재현율을 타협
- $ef$ 값을 $efConstruction$과 $K$ 중 큰 값으로 시작
- 값을 늘려가며 응답 시간과 재현율을 타협
Appendix(Source Code)
searchKnn
std::priority_queue<std::pair<dist_t, labeltype >>
searchKnn(const void *query_data, size_t k, BaseFilterFunctor* isIdAllowed = nullptr) const {
std::priority_queue<std::pair<dist_t, labeltype >> result;
if (cur_element_count == 0) return result;
tableint currObj = enterpoint_node_;
dist_t curdist = fstdistfunc_(query_data, getDataByInternalId(enterpoint_node_), dist_func_param_);
for (int level = maxlevel_; level > 0; level--) {
bool changed = true;
while (changed) {
changed = false;
unsigned int *data;
data = (unsigned int *) get_linklist(currObj, level);
int size = getListCount(data);
metric_hops++;
metric_distance_computations+=size;
tableint *datal = (tableint *) (data + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
tableint cand = datal[i];
if (cand < 0 || cand > max_elements_)
throw std::runtime_error("cand error");
dist_t d = fstdistfunc_(query_data, getDataByInternalId(cand), dist_func_param_);
if (d < curdist) {
curdist = d;
currObj = cand;
changed = true;
}
}
}
}
std::priority_queue<std::pair<dist_t, tableint>, std::vector<std::pair<dist_t, tableint>>, CompareByFirst> top_candidates;
bool bare_bone_search = !num_deleted_ && !isIdAllowed;
if (bare_bone_search) {
top_candidates = searchBaseLayerST<true>(
currObj, query_data, std::max(ef_, k), isIdAllowed);
} else {
top_candidates = searchBaseLayerST<false>(
currObj, query_data, std::max(ef_, k), isIdAllowed);
}
while (top_candidates.size() > k) {
top_candidates.pop();
}
while (top_candidates.size() > 0) {
std::pair<dist_t, tableint> rez = top_candidates.top();
result.push(std::pair<dist_t, labeltype>(rez.first, getExternalLabel(rez.second)));
top_candidates.pop();
}
return result;
}
addPoint
tableint addPoint(const void *data_point, labeltype label, int level) {
tableint cur_c = 0;
{
// Checking if the element with the same label already exists
// if so, updating it *instead* of creating a new element.
std::unique_lock <std::mutex> lock_table(label_lookup_lock);
auto search = label_lookup_.find(label);
if (search != label_lookup_.end()) {
tableint existingInternalId = search->second;
if (allow_replace_deleted_) {
if (isMarkedDeleted(existingInternalId)) {
throw std::runtime_error("Can't use addPoint to update deleted elements if replacement of deleted elements is enabled.");
}
}
lock_table.unlock();
if (isMarkedDeleted(existingInternalId)) {
unmarkDeletedInternal(existingInternalId);
}
updatePoint(data_point, existingInternalId, 1.0);
return existingInternalId;
}
if (cur_element_count >= max_elements_) {
throw std::runtime_error("The number of elements exceeds the specified limit");
}
cur_c = cur_element_count;
cur_element_count++;
label_lookup_[label] = cur_c;
}
std::unique_lock <std::mutex> lock_el(link_list_locks_[cur_c]);
int curlevel = getRandomLevel(mult_);
if (level > 0)
curlevel = level;
element_levels_[cur_c] = curlevel;
std::unique_lock <std::mutex> templock(global);
int maxlevelcopy = maxlevel_;
if (curlevel <= maxlevelcopy)
templock.unlock();
tableint currObj = enterpoint_node_;
tableint enterpoint_copy = enterpoint_node_;
memset(data_level0_memory_ + cur_c * size_data_per_element_ + offsetLevel0_, 0, size_data_per_element_);
// Initialisation of the data and label
memcpy(getExternalLabeLp(cur_c), &label, sizeof(labeltype));
memcpy(getDataByInternalId(cur_c), data_point, data_size_);
if (curlevel) {
linkLists_[cur_c] = (char *) malloc(size_links_per_element_ * curlevel + 1);
if (linkLists_[cur_c] == nullptr)
throw std::runtime_error("Not enough memory: addPoint failed to allocate linklist");
memset(linkLists_[cur_c], 0, size_links_per_element_ * curlevel + 1);
}
if ((signed)currObj != -1) {
if (curlevel < maxlevelcopy) {
dist_t curdist = fstdistfunc_(data_point, getDataByInternalId(currObj), dist_func_param_);
for (int level = maxlevelcopy; level > curlevel; level--) {
bool changed = true;
while (changed) {
changed = false;
unsigned int *data;
std::unique_lock <std::mutex> lock(link_list_locks_[currObj]);
data = get_linklist(currObj, level);
int size = getListCount(data);
tableint *datal = (tableint *) (data + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
tableint cand = datal[i];
if (cand < 0 || cand > max_elements_)
throw std::runtime_error("cand error");
dist_t d = fstdistfunc_(data_point, getDataByInternalId(cand), dist_func_param_);
if (d < curdist) {
curdist = d;
currObj = cand;
changed = true;
}
}
}
}
}
bool epDeleted = isMarkedDeleted(enterpoint_copy);
for (int level = std::min(curlevel, maxlevelcopy); level >= 0; level--) {
if (level > maxlevelcopy || level < 0) // possible?
throw std::runtime_error("Level error");
std::priority_queue<std::pair<dist_t, tableint>, std::vector<std::pair<dist_t, tableint>>, CompareByFirst> top_candidates = searchBaseLayer(
currObj, data_point, level);
if (epDeleted) {
top_candidates.emplace(fstdistfunc_(data_point, getDataByInternalId(enterpoint_copy), dist_func_param_), enterpoint_copy);
if (top_candidates.size() > ef_construction_)
top_candidates.pop();
}
currObj = mutuallyConnectNewElement(data_point, cur_c, top_candidates, level, false);
}
} else {
// Do nothing for the first element
enterpoint_node_ = 0;
maxlevel_ = curlevel;
}
// Releasing lock for the maximum level
if (curlevel > maxlevelcopy) {
enterpoint_node_ = cur_c;
maxlevel_ = curlevel;
}
return cur_c;
}
References
- Yu. A. Malkov, D. A. Yashunin. “Efficient and robust approximate nearest neighbor search using Hierarchical Navigable Small World”. IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence. 2018. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.09320.
- Github. nmslib. “hnswlib”. https://github.com/nmslib/hnswlib.
- Daniel@World. 2019.04.01. “Navigable Small World Graphs for Approximate Nearest Neighbors: Implementation in Rust and Time Series Experiments.”. http://daniel-at-world.blogspot.com/2019/04/navigable-small-world-graphs-for.html.
- GeeksforGeeks. 2024.06.18. “Greedy Best First Search Algorithm”. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/greedy-best-first-search-algorithm/.
- Medium. Vyacheslav Efimov. 2023.06.16. “Similarity Search, Part 4: Hierarchical Navigable Small World”. https://towardsdatascience.com/similarity-search-part-4-hierarchical-navigable-small-world-hnsw-2aad4fe87d37.
- 잉여의 생각저장소. 2023.02.07. “Lucene ANN 분석1 - HNSW Algorithm”. https://chocolate-life.tistory.com/11.
- NHN Cloud. NHN Cloud 로그플랫폼 개발팀 권성재. 2023.01.04. “[NHN FORWARD 22] 대충? 거의 정확하다! 벡터 검색 엔진에 ANN HNSW 알고리즘 도입기 (feat. SWIG Golang)”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hCqF4tDPNBw&t=1050s


댓글남기기